Run-length encoding (RLE) is a type of data compression technique. It compresses data with repeating patterns, such as text or images with solid background areas. Hitachi initially patented this method in 1983, and it would become a standard solution for image compression until more recent techniques.
How Does Run-length Encoding Work?
Let’s take a simple black-and-white image like the “Deal with it” sunglasses meme.

What Is Run-length Encoding?
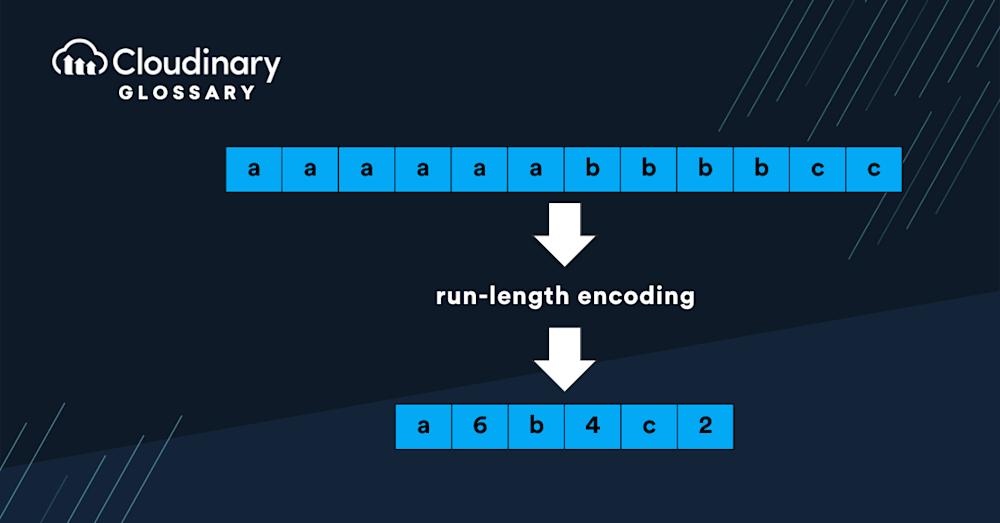
If we were to encode this, we would need to assign each color to a value. Let’s say that white pixels will be A, and black pixels will be B. Our encoder will take that information and reduce the image from 600 white pixels on the first row to A600, then repeat the same until it reaches another color. Then, it’ll count how many pixels are that color, add it to the sequential list, and continue until it’s complete.
As you can see, it’s simple in application but can quickly get out of hand with larger files or those with more color, which makes run-length encoding a tricky method in modern times, as it can make compressed images larger than their original.
Optimize Your Images with Cloudinary
If you want to optimize your images, run-length encoding is not for you. Instead, you should be using Cloudinary. Our Media Experience Cloud can help organize your digital media, encode your media with modern encoding techniques, and maintain high quality.
What are you waiting for? Get started with Cloudinary with a free account and unlock your media’s true potential.
Additional Resources You May Find Useful: