What Is HLS Streaming?
HLS, or HTTP Live Streaming, is a streaming protocol developed by Apple for delivering audio and video content over the Internet. Picture it like a conveyor belt: HLS breaks the content into small, manageable chunks, ready for transportation. It then delivers these data packets to your device via HTTP, the same transfer protocol that your web browser uses for loading regular web pages.
What sets HLS apart, though, is its ability to adapt to varying network conditions automatically. Like a smart traffic system that routes cars based on road conditions, HLS switches between different levels of quality, or ‘bitrates’, ensuring a smooth streaming experience even when internet speed fluctuates. This ensures a continuous stream, free from buffering interruptions, and offers the highest possible video quality that matches your current internet speed.
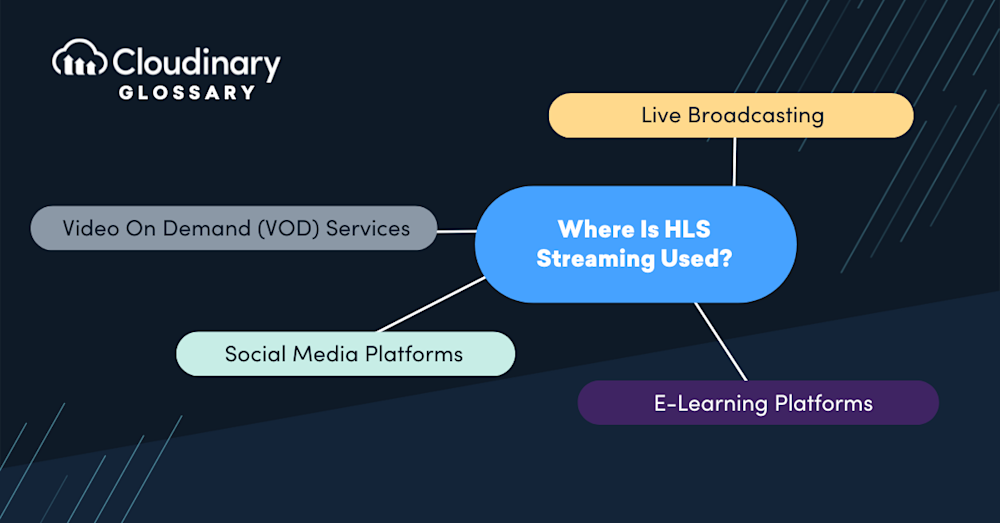
Where Is HLS Streaming Used?
HLS Streaming has become the go-to method for online video and audio content due to its versatility and adaptability. Its ubiquity is largely because it meets the demands of various applications and platforms, ensuring a seamless streaming experience regardless of device or internet stability. Some common use cases include:
- Live Broadcasting – Events like sports matches, concerts, and news are live-streamed using HLS to provide real-time content to audiences worldwide.
- Video On Demand (VOD) Services – Platforms like Netflix, Hulu, and Disney+ rely on HLS to deliver movies and TV shows in a quality that matches the viewer’s internet speed.
- Social Media Platforms – For live streaming features on platforms such as Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter, HLS allows users to broadcast and view content with minimal delays.
- E-Learning Platforms – HLS enables educational content to be accessible at various quality levels, ensuring that learning is uninterrupted, regardless of bandwidth constraints.
These are just a few examples, but they show the broad adoption and flexibility of HLS streaming across different internet-based services. It’s an essential technology that powers much of the media we consume daily, highlighting its importance in our continuously digital world.
How Does HLS Streaming Work?
HLS streaming operates by breaking down a video stream into a sequence of small HTTP-based file downloads, enabling efficient and adaptable video delivery over a wide range of network conditions. Here’s a simplified breakdown of how it works:
- Segmentation – The original video content is divided into short segments of equal length, typically ranging from 2 to 10 seconds. Each segment is then encoded at various quality levels to accommodate different bandwidths and device capabilities.
- Index File Creation – An index file (playlist) is generated, listing the URLs of these segments in sequence. This file also updates in real-time for live streaming, directing the player to the newest segment of the live feed.
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming – The player selects the most appropriate quality level based on the user’s current internet speed and device performance. It can switch between different quality streams as network conditions change, ensuring an uninterrupted viewing experience.
- Continuous Playback – As the video plays, the player downloads the segments in sequence, decoding and displaying them to the viewer. The player continually updates the playlist for live streams to include new segments, providing a seamless live viewing experience.
By leveraging standard HTTP transactions, HLS streaming maximizes compatibility with existing internet infrastructure, including firewalls and CDN networks, making it a versatile and reliable choice for distributing video content across various platforms and devices.
Pros and Cons of HLS Streaming
HLS Streaming, like any technology, comes with its own set of advantages and limitations. Understanding these can help you make informed decisions when implementing streaming solutions. Let’s dive into some of the key points:
Pros:
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming – Automatically adjusts the video quality to match the viewer’s internet speed, ensuring an uninterrupted viewing experience.
- Wide Compatibility – HLS is supported on a vast range of devices and browsers, making it a universal solution for content delivery.
- Robust and Reliable – It uses standard HTTP protocols, which can easily traverse firewalls and proxies, offering a high degree of reliability and performance.
Cons:
- Higher Latency – Compared to some other protocols, HLS can introduce a delay, which might not be optimal for real-time applications like online gaming or auctions.
- Increased Storage and Bandwidth Needs – Storing multiple bitrate versions of content requires more server space and bandwidth, potentially increasing costs.
- Complexity in Encoding – Preparing content in various bitrates and chunks adds a layer of complexity to the content creation and management process.
Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for anyone looking to integrate HLS streaming into their platform. It offers a fantastic user experience under the right conditions but requires careful consideration of its implications on your technical infrastructure and content management practices.
Final Thoughts
HLS streaming has revolutionized the video streaming industry by providing users with a seamless and adaptive streaming experience. Its versatility and ease of use have made it the preferred streaming protocol for many content providers, including live event streamers and video-on-demand services. While HLS comes with its fair share of pros and cons, its advantages undoubtedly outweigh its disadvantages in most cases.
Cloudinary provides an end-to-end solution for video streaming, offering a range of video management and optimization features, including support for various video formats. Take your digital experience to the next level with Cloudinary’s powerful media optimization tools. Sign up for free today!