What Is an F4V File?
An F4V file is a digital container format, similar to the FLV file, that was developed by Adobe Systems Incorporated. It’s part of the Flash Video family, including the FLV file. F4V files leverage the ISO-based media file format and are a more recent and advanced version of the older FLV format.
While Adobe’s F4V files were initially designed for usage in the Adobe Flash Player, their benefits also extend to other media players. On the practical side, this means you can play an F4V file on most modern multimedia players without a hitch.
But, with the phasing out of Adobe Flash Player at the end of 2020, the use and relevance of F4Vs are increasingly tied to these other players.
Should You Use F4V Files?
Deciding whether to use F4V files in your multimedia projects boils down to your specific video quality and compatibility needs. The F4V format, thanks to its support for H.264 and AAC codecs, provides high-quality video and audio, making it suitable for projects where clarity and detail are paramount.
For instance, if your task involves delivering HD content to an audience through platforms that support the format, F4V is an excellent choice. It’s also worth noting that if you’re dealing with legacy content originally produced in F4V format, maintaining the original file type can be useful to avoid losing quality during conversion.
However, considering the waning support for Adobe Flash technology, it’s crucial to look at the broader ecosystem of media playback and distribution. Many modern applications and devices favor newer formats like MP4, which shares the same foundational technology as F4V but is more widely supported and recognized as a standard across various platforms.
How Can You Open an F4V File?
While Adobe Flash Player was one of the primary tools for playing F4V files, its end doesn’t mark the end of F4V compatibility. Multiple software options exist that can handle an F4V file, thanks to their support for the H.264 video and AAC audio codecs. Here’s a list of applications and tools you can use to open and play your F4V files:
- VLC Media Player: A flexible, open-source media player that supports a wide array of formats including F4V.
- MPC-HC (Media Player Classic – Home Cinema): This light-weight media player is compatible with F4V files and can be run on even older hardware.
- PotPlayer: Much liked for its customizable features, PotPlayer also supports F4V files.
- Adobe Animate: Still within Adobe’s suite, Animate continues to support all Flash formats.
Remember to maintain updated versions of these players to enjoy the best compatibility and security. Importantly, always be cautious about what media files you open, especially if they are from an untrusted source, to ensure safety.
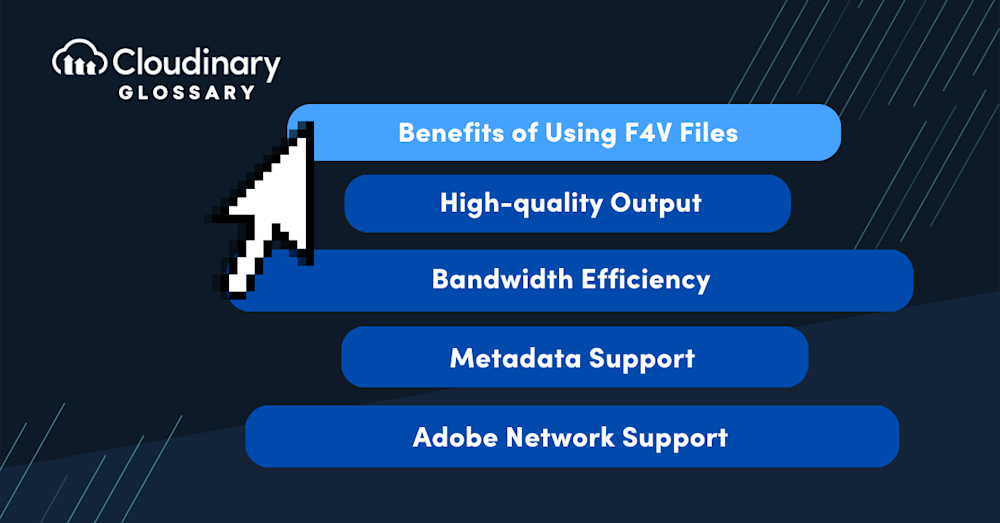
Benefits of Using F4V Files
There are distinct benefits to using F4V files in certain scenarios, despite the shifts in technology trends. Let’s consider what might tip the balance in favor of F4V files:
- High-quality Output – The ability of F4V files to use the H.264 video codec and AAC audio codec allows for high-definition video and high-quality audio, making these files potentially beneficial in contexts where quality is paramount.
- Bandwidth Efficiency – F4V files encoded with the H.264 video codec are efficient in their use of bandwidth, allowing for smoother streaming experiences even with high-quality content.
- Metadata Support – The F4V format supports extensive metadata, which could be useful for content management, searchability, and interactivity.
- Adobe Network Support – For projects relying on the Adobe ecosystem, using F4V files can offer seamless integration and compatibility.
Keep in mind that while these benefits might make F4V files appealing, context is key. Understanding your specific requirements and aligning them with the format’s strengths is crucial when deciding on implementing F4V files in your multimedia projects.
Downsides of Using F4V Files
Though F4V files have their specific uses and strengths, they come with a set of limitations that are important to consider when deciding on a media format. Let’s break down some of the key downsides:
- Decreasing Compatibility – As the web moves away from Flash-based technologies, fewer platforms support the playback of F4V files natively. This may necessitate additional steps for conversion or the use of specific legacy players.
- Industry Shift to HTML5 – The industry’s shift towards HTML5 for multimedia streaming reduces the practicality of using F4V, as HTML5 videos are typically in formats like MP4, WebM, or Ogg, which are more universally compatible.
- Obsolete Technology – With the discontinuation of Adobe Flash Player, F4V files are linked to what’s now considered an obsolete technology, increasing the risk of future incompatibility and potential security concerns.
- Limited Editing Software Support – F4V files are not as widely supported in video editing software, potentially complicating post-production processes or requiring format conversion.
Weighing these points, technical professionals must strategically consider the long-term usefulness and viability of using F4V files in their projects. It balances current needs for video quality and the practicality of file format longevity and support.
Final Thoughts
While the F4V format holds its specific merits, particularly in high-definition video quality and efficient bandwidth usage, one needs to weigh these against the broader industry move towards more versatile and widely-supported formats. The choice of media format can significantly influence user experience, resource accessibility, and the long-term viability of content, making this decision more strategically important than ever.