What is Spatial Compression?
Spatial compression, also known as lossless compression, is a technique used to reduce image file size without sacrificing visual information or quality. Unlike lossy compression, which involves discarding certain parts of the image data, spatial compression preserves all the original data by leveraging statistical redundancies and mathematical algorithms to store the image more efficiently.
The key idea behind spatial compression is to exploit an image’s spatial correlation and patterns. By identifying and encoding redundant information, spatial compression algorithms significantly reduce the number of bits required to represent the image, resulting in smaller file sizes.
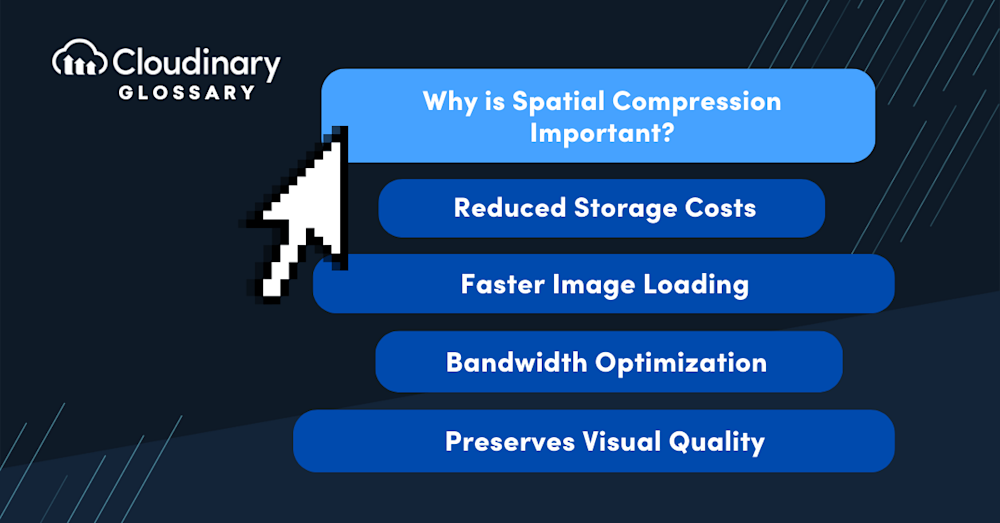
Why is Spatial Compression Important?
Spatial compression offers several benefits that make it crucial in optimizing image storage and delivery:
- Reduced Storage Costs – With the proliferation of digital images, managing and storing large image files can become expensive. Spatial compression allows for a significant reduction in file sizes, resulting in reduced storage costs and more efficient use of resources.
- Faster Image Loading – Smaller image file sizes mean faster loading times, improving user experiences on websites and mobile applications. Spatial compression enables seamless and quick image delivery, enhancing performance and engagement.
- Bandwidth Optimization – In cases where data transfer is limited or costly, spatial compression becomes essential. Smaller image files consume less bandwidth, allowing faster and more economical data transfers, especially in situations with low network speeds or expensive data plans.
- Preserves Visual Quality – One of the significant advantages of spatial compression is its ability to maintain the original visual quality of images. By preserving all the image data, spatially compressed images retain their integrity and fidelity, ensuring a visually appealing user experience.
Pros and Cons of Spatial Compression
Like any technique, spatial compression has its pros and cons:
Pros
- Lossless Compression – Spatial compression preserves the original image data and visual quality without loss. It is ideal for scenarios where image fidelity is crucial, such as medical imaging or archival purposes.
- Efficient Storage – By significantly reducing file sizes, spatial compression optimizes storage requirements and enables cost savings while providing access to a large collection of images.
- Fast Loading – Smaller file sizes resulting from spatial compression lead to faster image loading times, enhancing user experiences and satisfaction.
- Perfect Reproduction – Since spatial compression retains all the original data, the decompressed image replicates the original, ensuring accurate reproduction.
Cons
- Limited Compression Ratios – Spatial compression typically achieves lower compression ratios compared to lossy compression. While this maintains image quality, it may not provide the same level of file size reduction as lossy techniques.
- Higher Storage Overheads – To achieve lossless compression, spatial compression may require larger storage overheads than lossy compression methods, which discard some image data.
- Less Effective for Natural Images – Spatial compression algorithms may be less effective for images with complex patterns or natural scenes, as they may have limited spatial redundancies.
Final Thoughts
Spatial compression is a powerful technique that optimizes image storage and delivery by reducing file sizes while preserving the original image data and visual quality. With benefits such as reduced storage costs, faster loading times, and bandwidth optimization, spatial compression has become essential in today’s digital landscape.
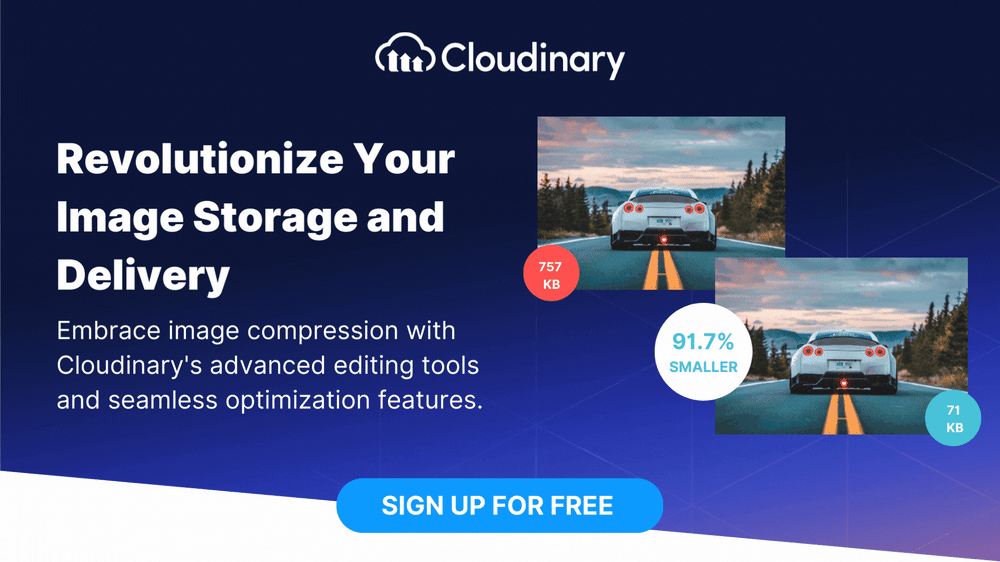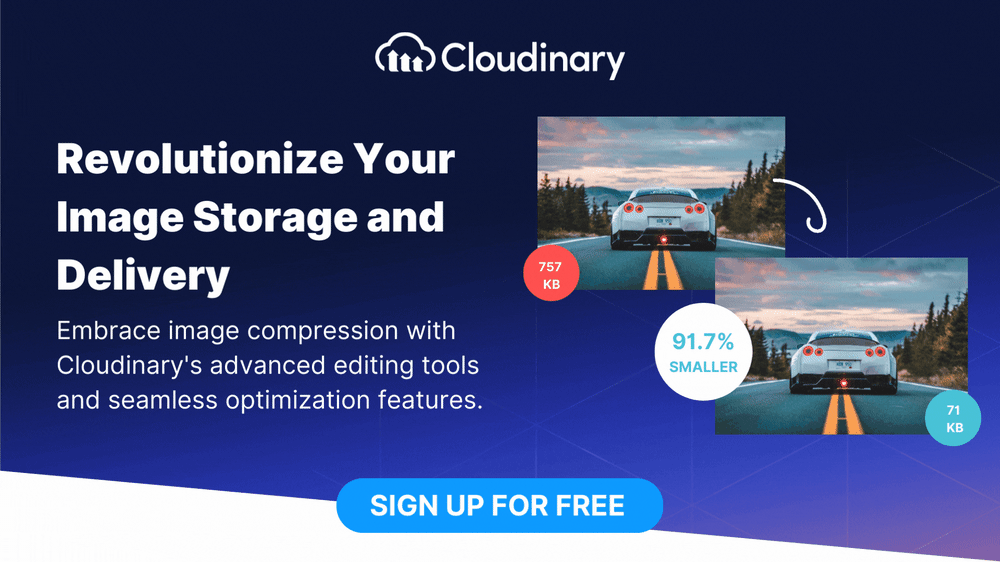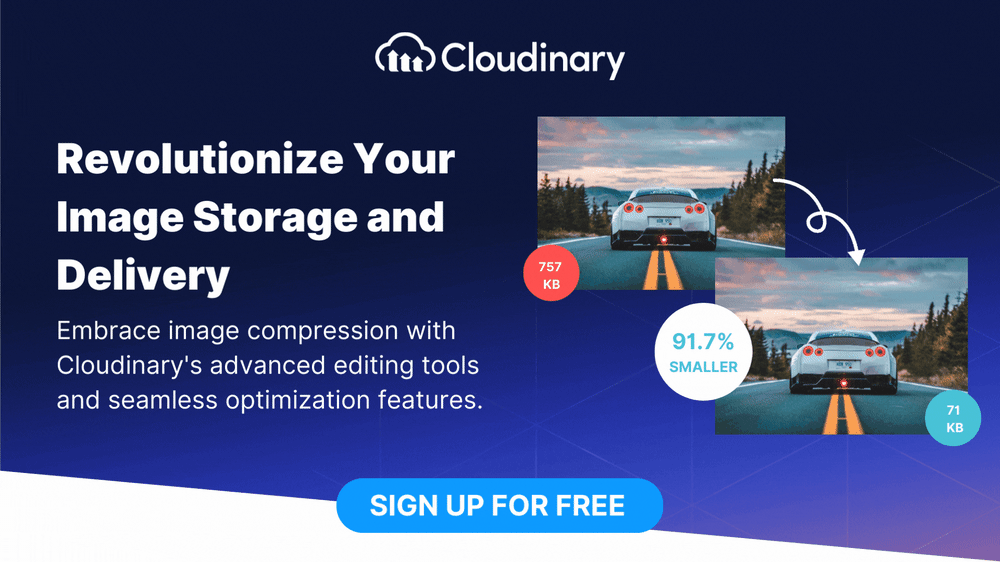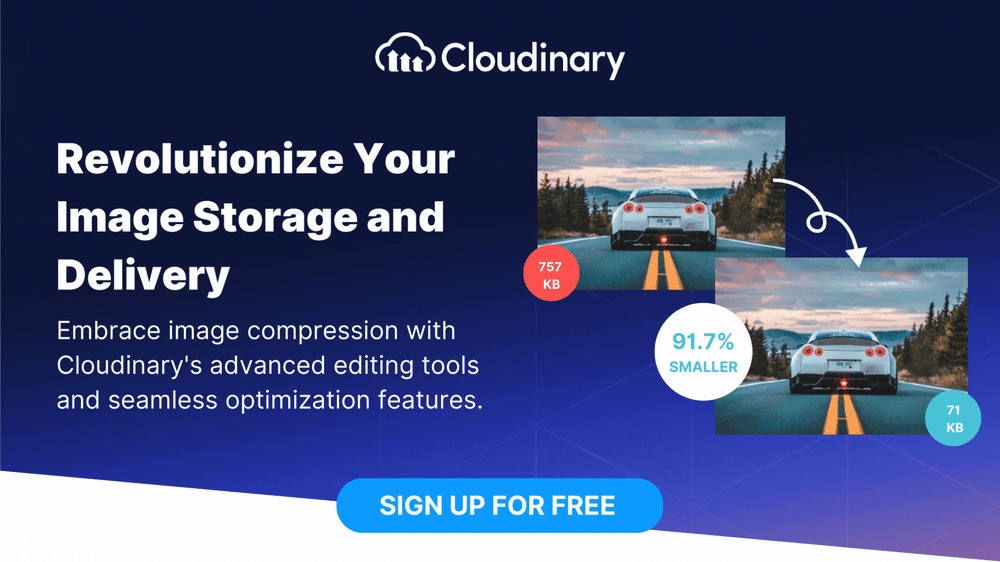
Enhance your image storage and delivery workflows, and consider utilizing the capabilities of a comprehensive media management platform like Cloudinary. Unlock the full potential of your digital content with Cloudinary’s advanced editing and optimization tools. Sign up today.