What Is Drop Frame?
Drop frame is a timecode method that maintains synchronization between video and audio in video editing and broadcast. It compensates for the difference between the exact duration of time (24 hours) and the time calculated from the standard frame rate (29.97 frames per second). By dropping frames at specific intervals, drop frame timecode ensures that the displayed time remains accurate, even though the actual frame rate is slightly lower than the stated one.
In addition to its use in timecode synchronization, “drop frames” can also refer to instances where frames are skipped or repeated during video playback or streaming. This happens when the system or hardware cannot process the next frame in time, leading to noticeable disruptions in performance, such as repeated frames or lower frame rates. Understanding this broader use of the term is essential for professionals dealing with video production, streaming, and gaming environments.
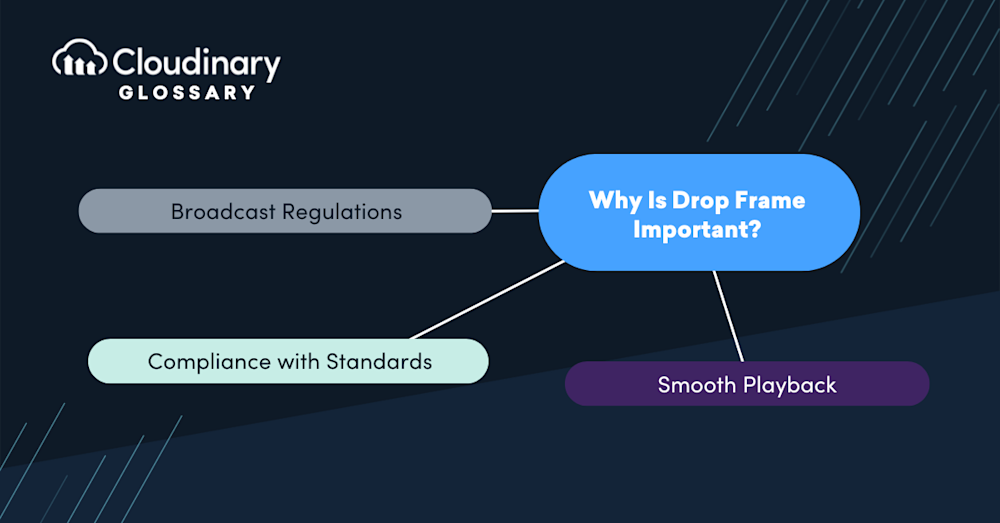
Why Is Drop Frame Important?
Drop frame timecode is critical in maintaining time accuracy within the video editing process. Here are a few reasons why drop frame is important:
- Broadcast Regulations – Broadcast television and other time-dependent applications rely on precise time synchronization. Drop frame timecode is essential for ensuring accurate timing in programs and advertisements, especially when adhering to fixed time slots.
- Compliance with Standards – Many professional video editing workflows and post-production processes follow industry standards that require the use of drop frame timecode. This allows for consistent and accurate time representation in the final product.
- Smooth Playback – The use of drop frame timecode helps to establish a seamless viewing experience for the audience, as the occurrence of dropped frames is imperceptible to the human eye due to its insertion at regular intervals.
Beyond editing, dropped frames in a streaming or rendering context can disrupt the viewer experience by causing visible stutters or frame repetition. For example, when the 0.03-second difference in NTSC video (29.97 fps) adds up to one frame, a frame is dropped in timecode. Similarly, when hardware, encoding, or internet speed cannot keep up, frames are skipped or repeated during playback. Troubleshooting these issues often involves checking hardware (e.g., upgrading a computer or encoder), optimizing internet speed (e.g., switching to a wired connection), and refining stream settings. These steps are critical in ensuring smooth playback across platforms.
Drop Frame vs. Non-Drop Frame
To better understand the distinction between drop frame and non-drop frame timecode, let’s explore their differences:
- Frame Skipping – The primary variation lies in the handling of time representation. Drop frame timecode achieves synchronization by occasionally skipping frame numbers (dropping frames) without affecting the visual playback speed. On the other hand, the non-drop frame timecode increments the frame numbers consistently according to the frame rate.
- Time Accuracy – Drop frame timecode accurately represents the actual elapsed time, which is slightly shorter than the time calculated from the frame rate. In contrast, a non-drop frame timecode allows each frame to consume the same time duration, which results in a slight time discrepancy over extended periods.
- Usage Scenarios – Drop frame timecode is primarily used in applications that demand precise time synchronization, such as broadcast television, film editing, and professional video production. Non-drop frame timecode is commonly used in scenarios where exact time representation is less critical, such as web videos, non-linear editing systems, and personal video projects.
- Broader Context – In addition to timecode synchronization, drop frames in playback can arise from performance limitations in streaming or rendering workflows. These issues often stem from delayed frame submission to the graphics card or insufficient internet bandwidth. Addressing dropped frames in these contexts requires solutions tailored to the specific environment, such as optimizing hardware, software, or network resources.
Final Thoughts
Drop frame timecode plays a significant role in maintaining accurate time synchronization in video editing and broadcasting. Its adoption ensures compliance with industry standards, facilitates smooth playback, and guarantees precise time representation in time-sensitive applications. While both drop frame and non-drop frame timecode have their place, understanding their differences enables professionals to select the appropriate timecode method for their needs.
Moreover, recognizing the dual meaning of “drop frames” in both timecode and streaming contexts is essential for anyone working in video production, broadcasting, or live streaming. Advanced video editing software and media management platforms like Cloudinary offer powerful tools for managing timecode and optimizing playback performance. Incorporating troubleshooting strategies for frame skipping in rendering or streaming workflows ensures a smooth and professional experience across all video formats and platforms.
Advanced video editing software and media management platforms like Cloudinary offer powerful tools for timecode management, enabling efficient editing workflows and seamless synchronization between video and audio.