
What Is HLSe?
HLSe stands for HTTP Live Streaming Encryption, an extension of Apple’s well-known HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) protocol. HLSe adds a layer of security to traditional HLS by employing AES video encryption. This ensures that video content streamed via HLSe is protected and accessible only to authorized viewers.
Key Features of HLSe:
- Encryption-Powered Security: HLSe protects media files by encrypting them, rendering them unreadable to unauthorized parties
- Flexibility: It is compatible with most devices and browsers, as it builds on HLS technology, which is widely supported
- Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR): Like HLS, HLSe delivers content in chunks at varying resolutions based on the internet connection quality, offering a buffer-free experience even in low-bandwidth scenarios
HLSe is particularly useful to media providers, broadcasters, and platforms looking to safeguard their content from piracy or unauthorized access while ensuring a smooth user experience across devices.
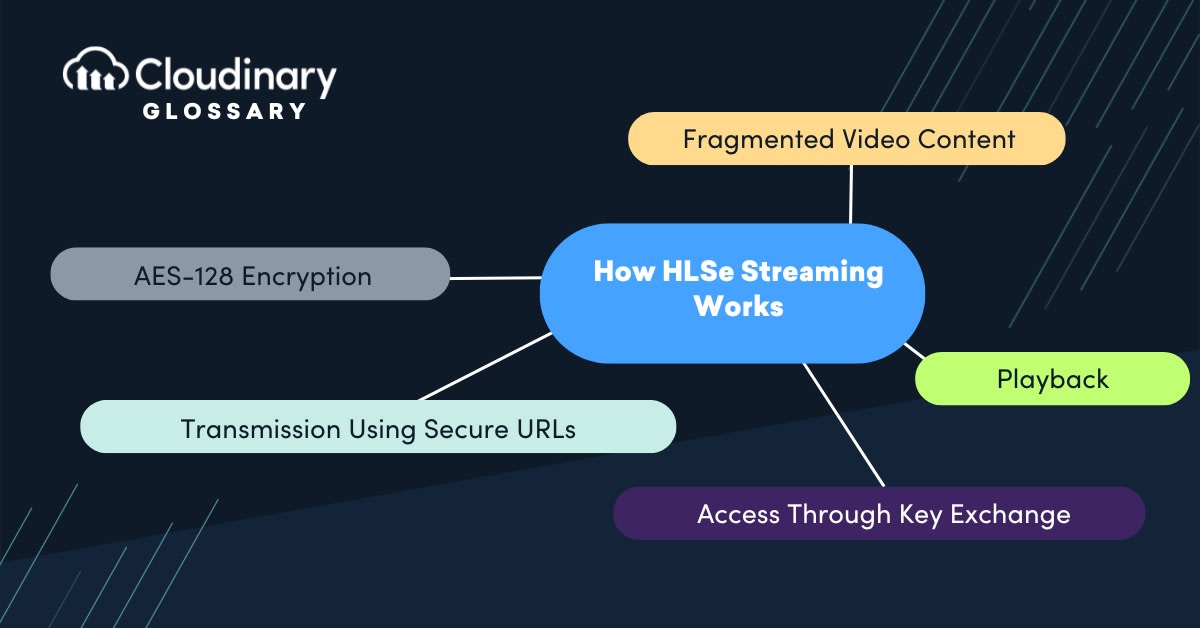
How Does HLSe Streaming Work?
To understand how HLSe streaming works, we need to break down its underlying mechanisms:
- Fragmented Video Content: Similar to standard HLS streaming, video content in HLSe is divided into small fragments (or “chunks”) that are delivered sequentially to viewers. Each chunk represents a short segment of the video (usually between 2-10 seconds).
- AES-128 Encryption: The video fragments are encrypted using AES-128 (Advanced Encryption Standard), which secures the content by turning it into an unreadable format. Encryption keys are generated on the server, and only authorized users can access them.
- Access Through Key Exchange: When a viewer requests access to a video file, their media player fetches the decryption keys from a secure URL. The keys are sent along with the chunks of content. Without these keys, the streamed video remains scrambled and unplayable.
- Transmission Using Secure URLs: The encryption keys are delivered using HTTPS connections to ensure the security of the transmission process.
- Playback: Once the content reaches the client device, the media player uses the encryption key to decrypt video fragments on the client side, allowing smooth playback of the content.
This process occurs in real time, ensuring both security and seamless streaming performance for the end user.
HLSe vs Other Streaming Protocols
HLSe shares similarities with other streaming protocols but distinguishes itself through its encryption-oriented focus. Let’s compare HLSe with some other popular streaming protocols:
1. HLSe vs HLS
- Security: While HLS provides adaptive streaming functionality, it lacks built-in encryption features. HLSe enhances HLS by embedding AES-128 encryption into streaming workflows, making content inaccessible to unauthorized users
- Compatibility: Both HLSe and HLS work on web browsers, mobile devices, smart TVs, and other platforms
2. HLSe vs MPEG-DASH
- Encryption Support: MPEG-DASH also supports encryption, but HLSe is often preferred for ease of implementation and wider browser compatibility, as DASH struggles on certain platforms (e.g., Safari)
- Adaptive Streaming: Both protocols offer ABR technology for buffer-free streaming
3. HLSe vs RTMP
- Security: RTMP (Real-Time Messaging Protocol) is less secure than HLSe, as it does not inherently support encryption
- Playback: RTMP does not deliver content in chunks, whereas HLSe relies on fragmented video delivery for adaptive streaming
HLS Encryption vs DRM
A major discussion in video streaming security revolves around HLSe and Digital Rights Management (DRM). While both aim to protect content, their approaches differ:
HLSe
HLSe applies AES-128 encryption directly to video fragments. Any device capable of playing HLS can process HLSe content without additional plugins or licenses. HLSe is lightweight and straightforward compared to DRM.
Digital Rights Management
DRM, such as Widevine, FairPlay, or PlayReady, offers a more comprehensive system that includes encryption, licensing, and usage controls. DRM provides finer control over playback restrictions like limiting the number of devices per account, enabling revocation of viewing rights, or setting expiry dates.
Key Differences Between HLS Encryption and DRM
Security Method
- HLSe uses AES-128 encryption to secure video fragments
- DRM adds encryption plus licensing for more comprehensive protection
Ease of Implementation
- HLSe is simple and easier to implement
- DRM is complex and requires specialized systems
Compatibility
- HLSe supports a wide range of devices and browsers due to its foundation in HLS
- DRM has limited compatibility, requiring devices or platforms that support specific DRM providers
Playback Control
- HLSe offers basic security and lacks advanced access restrictions
- DRM provides granular control, such as limiting the number of devices per account, revoking access, or setting playback expiration
Cost
- HLSe is affordable, ideal for lightweight security solutions
- DRM is expensive and requires more resources to implement and maintain
Advantages and Disadvantages of HLSe
Advantages
- Enhanced Content Security: AES-128 encryption prevents unauthorized access and protects content from piracy
- Wide Compatibility: HLSe supports a broad range of devices and browsers, owing to its foundations in HLS
- Quick Implementation: HLSe is easy to set up compared to more complex security protocols like DRM
- Adaptive Streaming: It retains the benefits of HLS, ensuring high-quality playback based on network conditions
- Cost-Efficient: As a lightweight security solution, implementing HLSe is affordable compared to DRM systems
Disadvantages
- Basic Security: While AES-128 encryption is robust, HLSe does not offer the granular control or advanced license management features of DRM
- Susceptible to Key Theft: If encryption keys are exposed or compromised, the system becomes vulnerable to hacks
- No Playback Restrictions: HLSe lacks the functionality to set limits on how content is accessed or shared (e.g., multiple device restrictions)
- Dependent on HTTPS: To secure key delivery, HLSe must operate over HTTPS protocols, requiring reliable SSL/TLS infrastructure
Last Thoughts
HLSe is a powerful protocol that efficiently combines adaptive video streaming with robust encryption. Its ability to deliver secure, high-quality media content has made it popular among streaming providers looking to prevent unauthorized use while providing seamless audience experiences.
However, HLSe is not without limitations. It’s best suited for situations in which basic encryption is sufficient rather than scenarios requiring advanced controls, like licensing and multiple-device restrictions. In these cases, DRM tends to be more effective but comes with increased costs and complexity.


