What Is Variable Bit Rate?
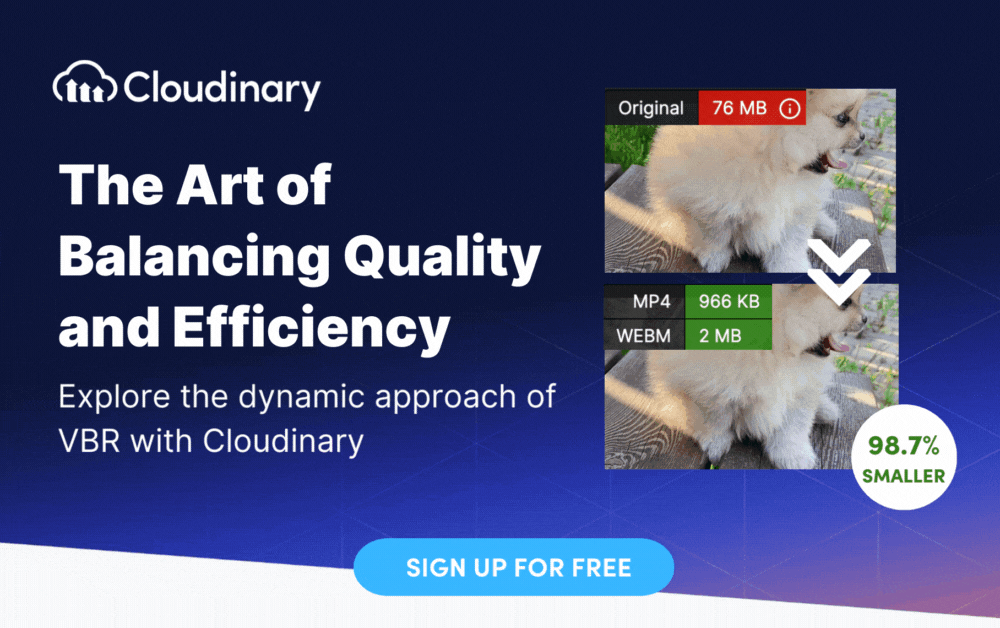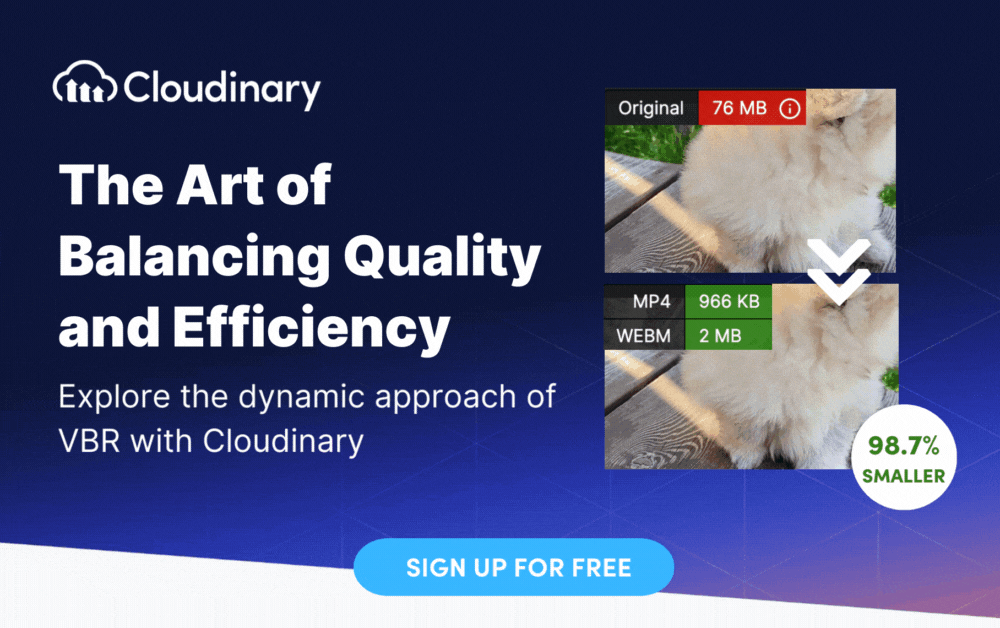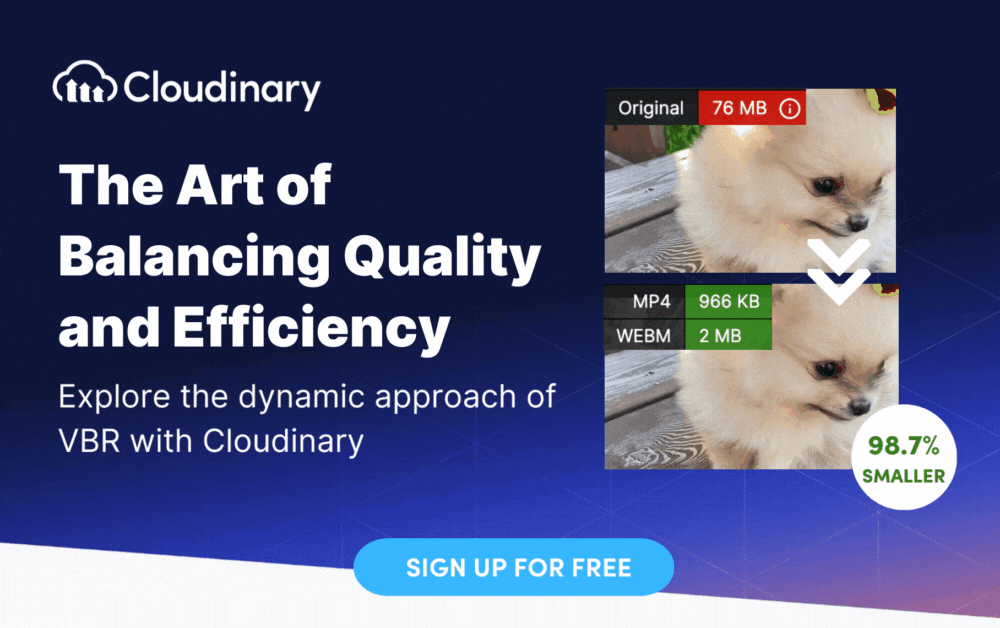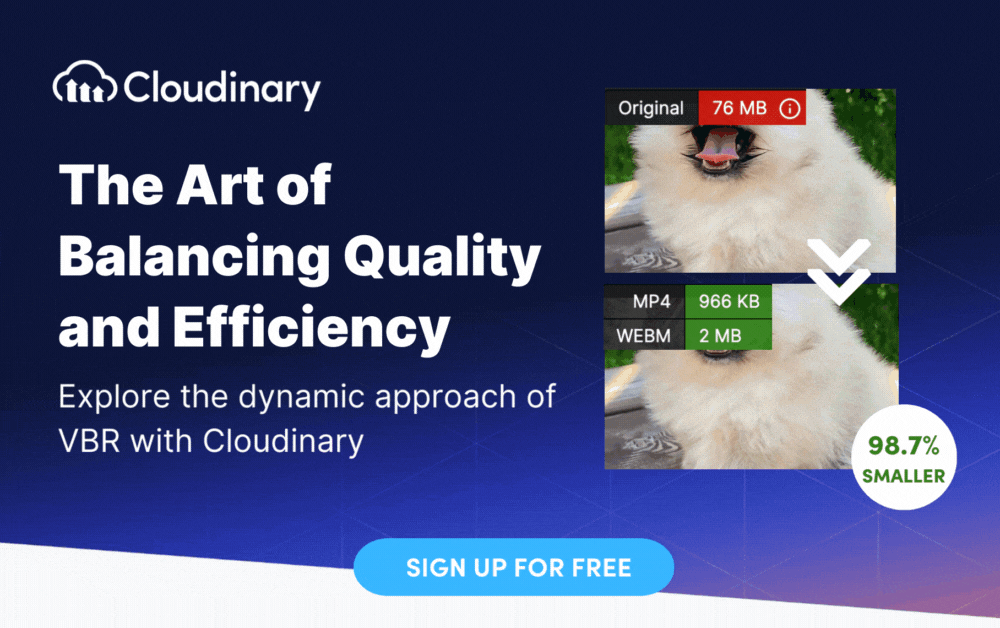
Variable Bit Rate (VBR) is a method of encoding digital audio or video data. The ‘Variable’ in its moniker indicates that the data rate and file size change over time, adjusting the output quality to match the complexity of the encoded data. So, when the data gets complex, VBR might pump up the data rate to maintain high quality; in contrast, for simpler data, it can reduce the rate, resulting in smaller file sizes.
In this orchestration of data, VBR is like a data conductor, fine-tuning the quality with the complexity of the digital performance it encounters. Its adaptability stands as its most significant benefit, offering a balance between quality and file size. This can be particularly handy when dealing with different scenes in a video or various elements in an audio track. Now, as we delve deeper, we’ll uncover the practical aspects of VBR along with its implications in the digital world.
How Does Bitrate Affect Video Quality?
Bitrate plays a crucial role in determining the quality of a video. It refers to the data per unit of time used to represent the video. Higher bit rates allow more data to be allocated to each frame, resulting in higher fidelity. On the other hand, lower bit rates can lead to compression artifacts, such as pixelation and blurring.
When using VBR, the variable allocation of bits ensures that scenes with high complexity receive more data, preserving details and minimizing compression artifacts. This results in a video with improved visual quality, even at lower overall bit rates.
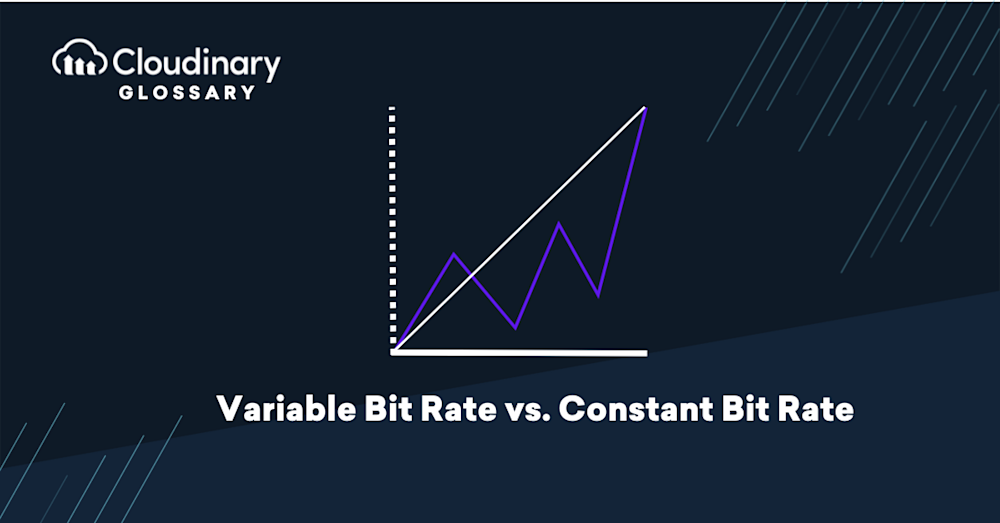
Variable Bit Rate vs. Constant Bit Rate
The key difference between VBR and CBR is their approach to allocating bits during encoding. While CBR maintains a fixed bit rate throughout the video, VBR intelligently gives more bits to complex scenes with high detail and fewer to less complex scenes with lower detail.
VBR offers several advantages over CBR. First, it allows for better preservation of video quality. By allocating more bits to detailed scenes, VBR ensures that fine details are captured accurately, resulting in more visually appealing videos. Additionally, VBR can reduce the overall file size of the video without compromising quality, making it ideal for streaming and storage purposes.
When To Use VBR or CBR
Deciding between Variable Bit Rate (VBR) and Constant Bit Rate (CBR) ultimately depends on your desired balance between file size, quality, and playback compatibility. To help you make an educated decision, we’ve listed some general guidelines below for when to use VBR or CBR:
- VBR:
- When prioritizing quality over a constant data rate.
- When distributing content online or streaming on-demand.
- When encoding complex and varying data, like music or videos with diverse scenes.
- When you need a more efficient use of storage or bandwidth.
- CBR:
- When uniform quality is needed for each part of a video or audio stream.
- When streaming content in real-time or for live broadcasts, where stability is essential.
- When encoding data that is relatively consistent in complexity.
- When compatibility across a wide range of playback devices or applications is crucial.
Advantages of Variable Bit Rates (VBR)
The use of Variable Bit Rates (VBR) in encoding audio and video files comes with a host of benefits, key among them include:
- Improved Quality-to-Space Ratio – VBR offers a superior quality-to-space ratio compared to Constant Bit Rate (CBR). It intelligently adjusts the bit rate to match the complexity of the data being encoded, using fewer bits for less demanding sections and more bits for challenging parts. This results in a more efficient use of storage space without compromising the quality of the audio or video.
- Optimal Use of Bandwidth – VBR ensures optimal use of bandwidth by dynamically adjusting the bit rate according to the complexity of the data. It ensures that complex data sections are given the necessary bit rate for high-quality output while reducing the bit rate for simpler sections, hence preventing wastage of bandwidth.
- Enhanced Audio and Video Quality – VBR delivers superior audio and video quality compared to CBR. By allocating more bits to complex sections of the data, VBR ensures that these sections are encoded at a higher quality, resulting in an overall better audio or video output.
- Efficient Storage Utilization – Since VBR uses fewer bits for less complex sections of the data, it results in smaller file sizes compared to CBR. This leads to more efficient storage utilization, especially in scenarios where storage space is a concern.
Disadvantages of Variable Bit Rates (VBR)
Despite these benefits, the use of VBR also has a few drawbacks, including:
- Longer Encoding Time – VBR takes a longer time to encode data compared to CBR. This is because VBR uses a more complex process that involves analyzing the complexity of the data and adjusting the bit rate accordingly. This extra time can be a disadvantage in time-sensitive applications.
- Limited Compatibility – VBR encoded files may not be compatible with some older hardware or software. This is because these older systems were designed to work with CBR and might not support the dynamic adjustment of bit rate that VBR uses.
- Inconsistency in Quality – While VBR generally delivers higher quality audio and video, it can sometimes result in inconsistent quality. This is especially true in scenarios where the complexity of the data changes rapidly, causing the bit rate to fluctuate.
- Complexity in Streaming – Streaming VBR encoded files can be more complex compared to CBR files. This is because the bit rate changes dynamically in VBR, requiring more sophisticated streaming protocols to ensure smooth playback.
Pro TipConsider Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
Adaptive bitrate streaming is a video delivery technique that adjusts the quality of a video stream in real time according to detected bandwidth and CPU capacity. This enables videos to start quicker, with fewer buffering interruptions, and at the best possible quality for the current device and network connection, to maximize user experience.
Wrapping Up
To sum it all up, deciding whether to employ VBR or CBR in your project will hinge on the specific demands of quality, file size, and playback consistency. Both encoding methods have advantages and appropriate use cases, so taking the time to understand your project’s requirements is crucial. With a clear comprehension of the differences and limitations of each approach, you’ll be better equipped to make informed decisions that cater to your project’s unique needs to deliver exceptional results.
With a suite of powerful features and a user-friendly interface, Cloudinary simplifies managing your digital assets, ensuring that your content is optimally tuned for performance and quality.
So, why wait any longer? Embrace the future of media with Cloudinary, and elevate your projects to new heights!