What is Video Rendering?
At its core, video rendering is a dynamic process that combines the raw elements of a video project into a final product that viewers can play back on a display. Picture assembling a jigsaw puzzle. Each piece of that puzzle could represent a different element in the video. When all these puzzle pieces are correctly connected, we get a full, detailed picture or, in this case, a watchable video.
Rendering doesn’t just combine visuals; it’s also responsible for integrating audio and compressing the final output into a manageable size. This includes mixing video tracks for each frame, adding audio layers, and encoding the video using specific codecs that determine file size and playback quality.
The rendering process goes beyond simply joining these elements. It involves encoding the video to a desired format that could be played on specific devices or streaming platforms. During rendering, your video editing software does all the math, calculating how each pixel should appear based on the edits you’ve made, the effects you’ve added, the color grading applied, and the format you’ve chosen.
How Does Video Rendering Work?
Video rendering is like baking a cake: individual ingredients, combined with care and precision, create a delightful end product. Let’s explore a high-level summary of the key elements of video rendering:
- Raw Assets. These constitute the pillars of our project. They signify the unprocessed video clips, audio files, images, and other digital elements that make up your video.
- Editing Tools. These allow you to clip, fine-tune, synchronize your video materials, apply breathtaking special effects, and incorporate seamless transitions – often while previewing the results in real-time.
- Output Settings. Here, you determine the specific format, resolution, frame rate, and codecs that make your video file a perfect fit for your unique requirements – whether targeting a handheld mobile device or a streaming platform.
- Rendering Software. This is the actual tool that integrates all your prepared components and follows the designated settings to render your final video project.
- Mixing Tracks and Adding Audio. During rendering, the software combines individual video tracks on the timeline, processing them frame by frame to produce a cohesive visual output. Simultaneously, audio tracks are integrated, ensuring proper synchronization with the visuals. This step ensures that your video’s sound design—dialogue, music, or effects—aligns perfectly with the imagery.
- Encoding and Codec Selection. After the visuals and audio are mixed, the video is encoded to compress it into a smaller, more manageable file size. Choosing the right codec is essential here, as it directly impacts the output’s quality, size, and compatibility with playback devices.
- Quality Assurance. The final evaluation point is to ensure the delivered video matches the expectations, providing an opportunity for any last-minute adjustments committed to ensuring optimal video quality.
How Long Does Video Rendering Take?
The answer: it heavily depends on the ingredients in your mix. Like a recipe, your time will depend on your raw materials and the desired outcome. Rendering time is influenced by critical factors such as the complexity of the edits, the video format, length, resolution, the computing power of your hardware, and even the efficiency of your video editing software.
Let’s put some of these ingredients under a microscope. A video filled with intricate animations, special effects, and high resolution will inevitably take longer to render than a basic cut-and-trim project in a lower resolution. Mixing multiple video layers, incorporating high-quality audio, and encoding with advanced codecs add additional processing time. Similarly, a computer with a robust CPU and GPU, ample RAM, and SSD can navigate the rendering process faster and more efficiently than a less powerful one. And, not to forget, the choices made in output settings, such as the codec, also swing the rendering pendulum.
To put this into perspective, complex scenes requiring intense visual effects can take extraordinary amounts of time. For example, the black hole scene in Christopher Nolan’s Interstellar reportedly took 100 hours to render due to its intricate graphics and computations. This highlights the time-intensive nature of high-quality video rendering.
Video Rendering and Cloudinary
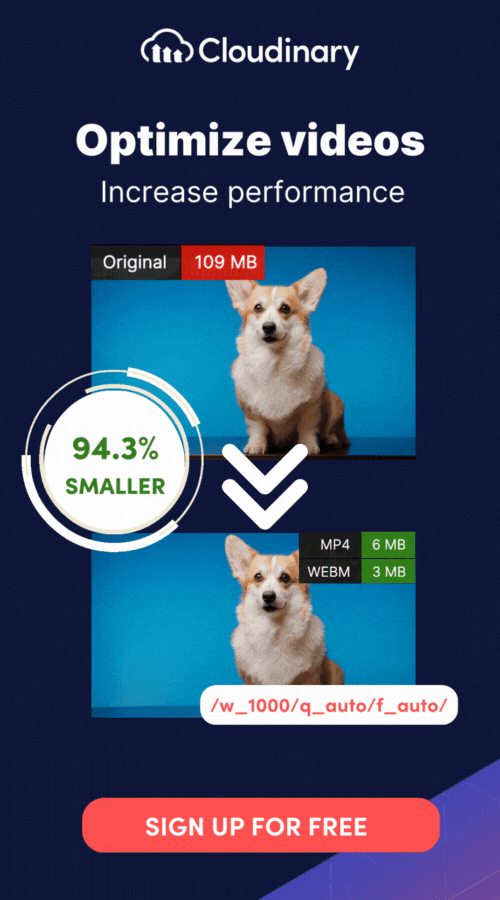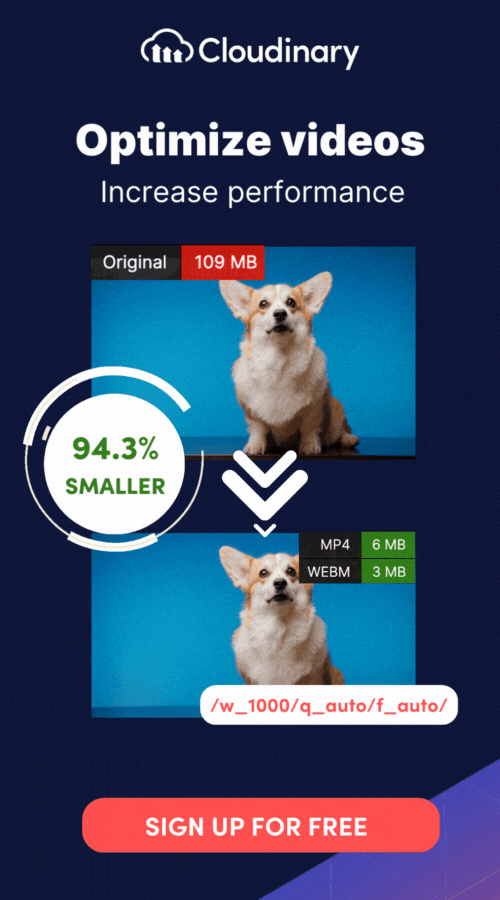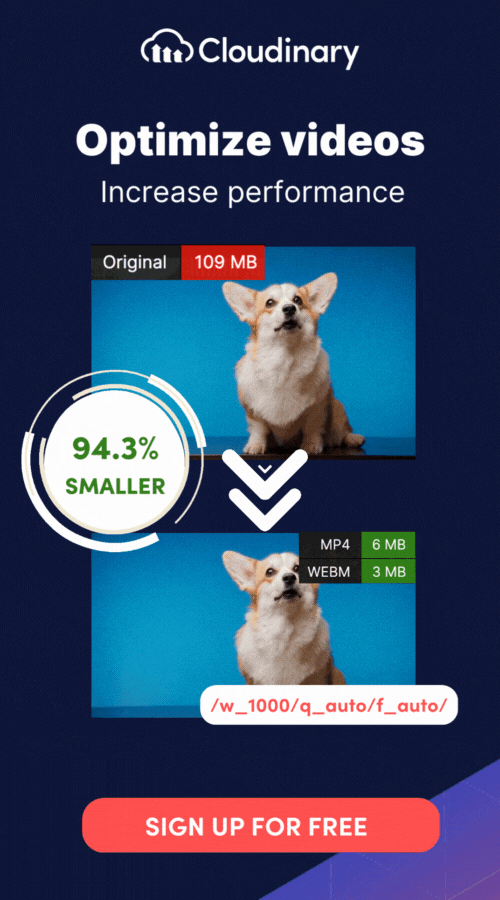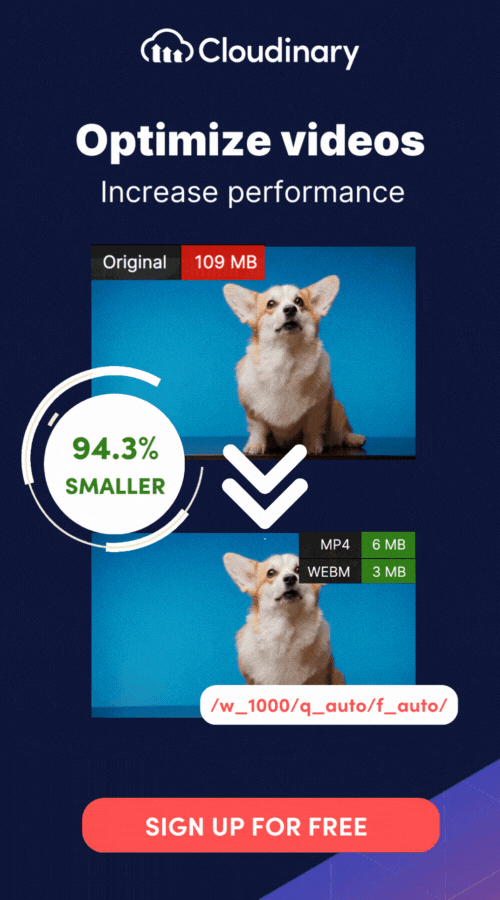
With Cloudinary, you can streamline your video rendering process, optimize video delivery, and achieve outstanding visual quality. Leverage Cloudinary’s robust infrastructure and cutting-edge technology to accelerate rendering times, ensure smooth playback, and deliver an exceptional user experience.
Cloudinary’s tools also simplify encoding and compression by offering advanced codec support and automated workflows, saving you time while ensuring the output file size and quality meet your requirements. Whether you need frame-by-frame processing, audio integration, or optimized streaming-ready formats, Cloudinary helps you manage these tasks efficiently.
Whether you’re an individual content creator, a marketing professional, or a business owner, Cloudinary provides the tools you need to enhance your video rendering workflow. Seamlessly integrate Cloudinary into your video production pipeline and unleash the true potential of your visual creations.
Additional Resources You May Find Useful:
- Convert Image to PNG
- Convert Image to AVIF
- Convert Image to WEBP
- Convert Image to JPG
- Convert Image to GIF
- Convert SVG to JPG
- Convert SVG to PNG
- Convert SVG to GIF
- Convert SVG to WEBP
- Convert SVG to AVIF
- Convert TIFF to JPG
- Convert TIFF to PNG
- Convert TIFF to GIF
- Convert TIFF to WEBP
- Convert HEIF to JPG