What Does Video Frame Rate Mean?
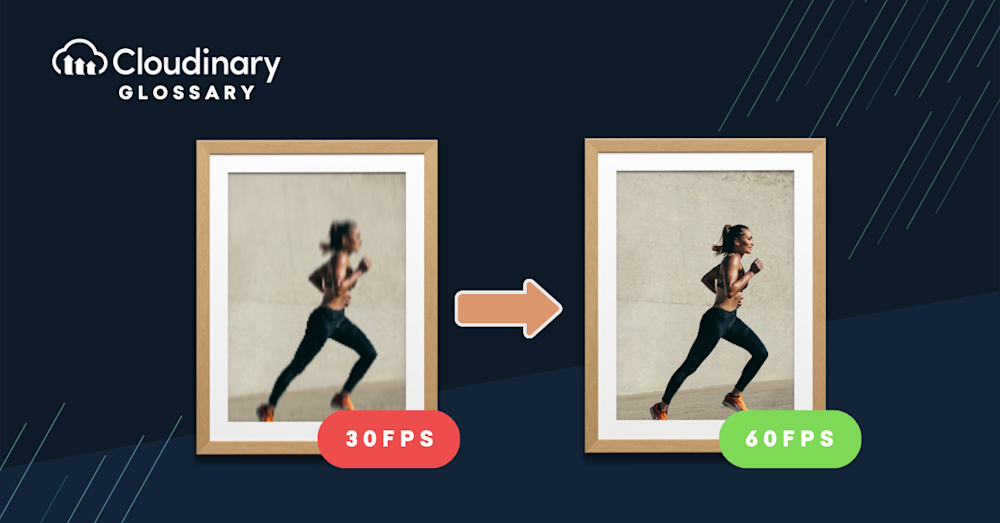
Frame rate is the number of video frames per second. For example, 30 fps means that 30 separate images are being shown every second to create one continuous moving picture. The higher the frame rate, the smoother and more lifelike your video will appear. In contrast, lower frame rates result in choppier motion and can make videos look like they’re being played at slow speed. With fast-moving subjects, low FPS can feel jerky or unnatural, though some creators embrace that look intentionally.
At its core, a video is simply a series of still images displayed in quick succession. The frame rate determines how quickly these images appear, creating the illusion of motion. This is why higher frame rates make movements look smoother and more natural.
What Are Common Video Frame Rates?
The most common frame rates you’ll come across include 24 FPS, 30 FPS, and 60 FPS. Each of these serves different purposes and fits various types of video content.
For instance, 24 FPS is the standard for most movies and gives that cinematic look we all recognize. At this frame rate, natural-looking motion blur contributes to the classic film-like quality. On the other hand, 30 FPS is widely used for TV broadcasts and online streaming, offering smooth, lifelike motion without the complexity of higher frame rates.
Stepping up to 60 FPS, this frame rate is often employed in video games and sports broadcasts. The increased number of frames results in notably smoother motion, which is crucial for fast-paced action. Higher frame rates like 120 FPS or even 240 FPS are also gaining traction, especially in advanced gaming and specialized filming techniques, but these are less common for everyday video production due to their increased demand on hardware and storage.
Which Video Frame Rate Should You Use?
Frame rates are measured in frames per second (fps). The standard frame rate for cinema is 24 fps; for television, it’s 30 fps; and for computer monitors, it’s 60 fps. High-end video games typically run at 120 fps or above.
Choosing the right frame rate depends heavily on the type of content and the intended audience. For instance, high-action videos and games benefit from higher frame rates, while slower-paced content, like romantic scenes or certain types of cinematic films, often looks best at 24 fps. Lower frame rates can also be used deliberately to create a more “dreamy” or stylized aesthetic in specific scenes.
Does The Frame Rate Affect The File Size of A Video?
The frame rate of a video refers to the number of frames per second (fps). The higher the frame rate, the smoother your video will look. However, this also means that each individual frame requires more storage space on your hard drive or in your project file–and, therefore, increases its file size.
It’s also worth noting that if you shoot a video at a high frame rate but display it at a lower rate (e.g., shooting at 120 fps but displaying at 30 fps), each frame will carry more detail, increasing file size significantly. Managing this effectively requires understanding both frame rate and resolution.
The lower your video’s fps setting (and thus higher resolution), the larger its file size will be: if you shoot at 120 fps but only display at 30 fps then each individual frame will take up more memory than if you were displaying all 120 frames at once.
Is Higher Video Frame Rate Good?
A higher video frame rate can be beneficial in certain scenarios, but it doesn’t automatically translate to better quality. While it doesn’t enhance resolution—your video will still be 1080p or 4K—it does capture more frames per second, resulting in smoother motion. This is useful for capturing fast-moving action with a lifelike feel or creating stunning slow-motion effects. However, for standard viewing, especially in cinematic settings, lower frame rates like 24fps are often preferred for their classic, film-like aesthetic. Ultimately, whether a higher frame rate is good depends on the specific purpose of your footage.
Pick the Right FPS with Cloudinary
Cloudinary is great for optimizing and delivering video and adapting it to accommodate the user’s device and network speed. You can set up the appropriate parameters in several ways without having to learn the nitty-gritty of frame rates and the related lingo.
Additional Resources You May Find Useful: