People want better video quality more than ever. Everyone, from developers to everyday users, looks for clear videos that play smoothly and load fast. But there’s a problem: better videos usually mean bigger files, which take up more space and are slower to download. That’s where HEVC comes in. But what is HEVC exactly? It gives great video quality without huge file sizes. Plus, it supports resolutions up to 8K UHD, making it a future-proof option for high-definition content. In this guide, we’ll learn more about HEVC and why it’s so helpful.
HEVC, also known as H.265, is not just a simple update to previous video compression standards; it fundamentally changes how videos are encoded and stored. It analyzes frames more efficiently, breaking them into Coding Tree Units (CTUs) rather than the traditional macroblocks used in H.264. This allows it to process large sections of a video frame at once, improving compression and quality.
HEVC is widely used in streaming and broadcasting, particularly for high-resolution content like 4K and 8K. It is compatible with key streaming protocols, such as MPEG-TS (MPEG Transport Stream) and RTSP (Real-Time Streaming Protocol), making it a strong choice for both live and on-demand video applications. These protocols ensure efficient delivery of HEVC-encoded content across different platforms, from online video services to professional broadcasting.
While HEVC (H.265) offers superior compression and video quality compared to H.264, it is not always the best choice. H.264 remains the industry standard for many platforms, and its broader compatibility makes it the preferred option for certain use cases. Understanding the differences between these two formats is key to choosing the right one.
In this article:
- What is a Video Codec?
- Optimizing Low-Latency Streaming with Advanced Video Compression
- What is HEVC?
- HEVC vs. Other Video Codecs
- How To Edit HEVC Files
- What Are HEVC’s Compression Capabilities?
- What Are HEVC’s Downsides?
- Opening HEVC Files
- Common Use Cases for the HEVC Codec
- Key Considerations When Implementing the HEVC Codec
- Optimize HEVC Video Files Automatically with Cloudinary
What is a Video Codec?
Let’s start by understanding what a video codec is. A codec is a software-based method used to compress and decompress video files.
Video codecs reduce the file size of video sequences, allowing them to use less storage and be transmitted more efficiently over the internet or through broadcasts. The more effectively a codec compresses and delivers video data, the higher the quality of the playback. On the receiving end, the codec decompresses the data so the video can be displayed on-screen.
Optimizing Low-Latency Streaming with Advanced Video Compression
Every time someone watches a TV show, shares a video online, or makes a FaceTime call, they’re streaming video, and streaming consumes a significant amount of data. That’s where video codecs come in. Efficient compression ensures we don’t overwhelm available internet bandwidth, allowing for smooth, high-quality video playback without lag.
One of the most advanced codecs available today is HEVC (High Efficiency Video Coding), also known as H.265. As the successor to H.264 (AVC), HEVC offers faster and more efficient compression, resulting in better video quality.
While AVC compresses video using macroblocks, HEVC uses coding tree units (CTUs), which process data more efficiently. This leads to smaller file sizes and reduced bandwidth requirements, key to enabling seamless, low-latency video streaming.
What is HEVC?
HEVC is a video compression standard designed to maximize storage efficiency. It’s a smart technology that compresses videos into minimal space without sacrificing quality. In more technical terms, it’s also known as H.265 and MPEG-H Part 2.
HEVC was a combined effort, co-developed by ISO/IEC MPEG (Moving Picture Experts Group) and ITU-T VCEG (Video Coding Experts Group) and earned its place in the tech lexicon around 2013.
HEVC allows for significantly smaller video file sizes while ensuring top-notch quality. HEVC-encoded streams are most often wrapped in familiar multimedia containers like MP4 and MOV. Imagine faster streaming, fewer storage woes, and a smoother user experience – that’s the promise of HEVC. Compared to its predecessor H.264 (AVC – Advanced Video Coding), HEVC offers better compression while maintaining high quality, making it ideal for streaming and storage efficiency.
In addition to its storage benefits, HEVC plays a key role in professional media and broadcasting. Many streaming services, television broadcasters, and video conferencing platforms rely on HEVC’s compression efficiency to deliver high-quality video over networks with limited bandwidth. Its compatibility with MPEG-TS ensures that it is widely used in traditional broadcasting and IPTV services, while RTSP support makes it effective for real-time applications like surveillance systems and live event streaming.
However, while HEVC is more efficient, it is not universally supported. Many online streaming platforms still use H.264 as the industry standard, and older devices may struggle to decode HEVC files. This means that while HEVC is ideal for high-resolution content like 4K and 8K, H.264 remains the more widely compatible option.
HEVC vs. Other Video Codecs
Alternatives such as AV1 and VP9 have emerged as cost-effective, royalty-free solutions. So, how does H.265 compare to AV1?
While both provide excellent compression, AV1 is designed to offer even greater efficiency, especially for streaming. Supported by industry leaders like Google, Amazon, and Netflix, AV1 is gaining traction for delivering high-quality video at lower bitrates without the licensing fees associated with HEVC.
VP9, developed by Google, also delivers strong performance but typically doesn’t match AV1’s compression capabilities. As the video streaming industry continues to prioritize cost efficiency and performance, these newer codecs are becoming increasingly relevant, especially in web-based and OTT streaming environments.
How To Edit HEVC Files
It’s important to not just think “what is HEVC”, but how you can use it to your advantage. Firstly, ensure your video editing software supports HEVC. Many of today’s prominent editing tools have adapted to HEVC and offer compatibility.
When you launch your editing software, importing an HEVC file is generally no different than importing any other file type. Drag and drop, make your edits, apply effects, or whatever your creative heart desires. However, be mindful that HEVC’s advanced compression might require more computing power. So, if you’re working on a little older machine, be patient and expect it to flex its muscles a bit.
Remember, while editing, the magic of HEVC lies in its compression abilities, not necessarily its editing features. So, once you’ve finished editing, consider the file format you’ll be exporting to, especially if compatibility and file size are concerns. If you encounter issues with software that doesn’t support HEVC editing, converting HEVC files to MP4 using tools like Descript can be a practical workaround.
If your editing workflow involves sharing files with others or exporting to platforms that don’t support HEVC, you may need to convert your files to H.264 for broader compatibility. While HEVC offers sharper image quality with fewer artifacts, many professional studios and online services still prioritize H.264 due to its widespread support.
What Are HEVC’s Compression Capabilities?
One of HEVC’s achievements is its compression capabilities. But how does it achieve this? Let’s break it down:
- Encoding an Initial Frame. HEVC begins by encoding an initial video frame, which acts as a reference point.
- Encoding Only What Changes. Instead of redundantly encoding every single frame, HEVC smartly encodes only the portions of the video that change from one frame to the next.
- Expanding the Look Area. HEVC increases the area it inspects for changes, ensuring it captures all variations, no matter how minute.
Compared to its predecessor, the H.264 codec, 4K videos encoded with HEVC can take up approximately 50% less storage space without compromising quality. Additionally, HEVC supports 8K UHD resolution, making it a crucial format for ultra-high-definition content.
This efficiency makes HEVC ideal for streaming because it can deliver the same quality as H.264 at a lower bitrate. However, the tradeoff is that decoding HEVC requires more processing power, which can be a challenge for some older devices.
However, there’s a small downside. Not all devices or platforms have caught up with HEVC. So, while 4K HEVC compresses better, it might not be as universally compatible as its 4K H.264 counterpart. Always keep compatibility in mind when deciding your final file format.
What Are HEVC’s Downsides?
Adopting HEVC allows for significant file size reductions without compromising video quality. However, as with most tech solutions, it has its challenges, and understanding them helps make informed decisions.
- Compatibility. While HEVC is revolutionary regarding compression, not all devices and platforms support it. Many older devices, or even some current ones with limited software updates, might stutter or fail to play HEVC files altogether. So, for broader accessibility, converting to a more universally accepted format, like H.264, might be beneficial.
- Editing and Software Limitations. Certain video editing tools might not be fully optimized for HEVC. If you often work with videos, you’d want to ensure that your footage is editable without hitches. Converting HEVC to a format your software handles without problems might save you time and frustration.
- Sharing and Distribution. When sharing videos, especially in professional settings, you might not always know the tech specs of the recipient’s device. When compatibility is vital, sending videos in more commonly accepted formats is safer.
- Industry Adoption. Although HEVC is an advanced codec, many online streaming platforms and studios still use H.264 as the industry standard. This is one of the main reasons HEVC adoption has been slower despite its superior compression capabilities.
Opening HEVC Files
The method for opening an HEVC file depends mainly on the device and software you’re using. However, on modern operating systems and with updated media players, playing HEVC files is typically straightforward.
- Windows: Recent versions of Windows 10 come with built-in support for HEVC. If you cannot open an HEVC file, you might need to download the HEVC Video Extension from the Microsoft Store.
- Mac: MacOS High Sierra and later versions natively support HEVC playback. Just ensure you’re updated to the latest OS.
- Mobile Devices: Most current smartphones can handle HEVC without issues. Consider using third-party media players that offer HEVC support if your phone struggles.
- Web Browsers: HEVC support in browsers is a bit hit or miss. While some browsers might play HEVC content natively, others might require extensions or plugins.
- Apple Devices: HEVC is natively supported on iPhone 7 or later, iPad (6th generation) or later, and iPad Pro (10.5-inch) or later, ensuring smooth playback on Apple’s ecosystem.
- Third-Party Media Players: If your default player doesn’t support HEVC, you can use VLC, MPV, DivX Player, 5KPlayer, PotPlayer, PowerDVD, MPC-HC, or HEVC Video Player X for playback.
Remember, converting your HEVC files to a more universally accepted format can be a practical solution if you often deal with compatibility issues.
Common Use Cases for the HEVC Codec
From live event broadcasting to OTT services and video conferencing, HEVC enables crisp visuals and seamless playback, even with limited bandwidth, making it ideal for 4K and 8K content distribution.
As more sectors, including gaming, education, and enterprise, embrace remote interaction, HEVC adoption continues to expand. The codec’s ability to deliver exceptional visuals while optimizing bandwidth makes it an essential tool for modern video experiences.
1. Live Streaming with Exceptional Quality
Live streaming is more popular than ever, and delivering a premium experience requires both low latency and highly efficient video compression.
HEVC significantly reduces average bitrates by up to 50% compared to older codecs, without compromising video quality. This makes it ideal for streaming high-resolution video over limited bandwidth connections.
By using HEVC, businesses can deliver smoother, high-quality live streams that are more accessible to a wider audience. Smaller file sizes allow faster transmission, minimizing lag and enhancing the overall viewer experience.
2. OTT (Over-the-Top) Content Delivery
OTT platforms such as Netflix, Hulu, and Amazon Prime Video depend on efficient video delivery to stream 4K content at scale. As high-resolution video becomes the standard, optimizing compression is critical to performance and cost-effectiveness.
HEVC enables high-efficiency streaming by reducing video file sizes and lowering bitrates, all while maintaining superior visual quality. This is especially important for live sports and premium entertainment content, where viewers expect flawless playback.
3. Enhanced Video Conferencing
Video conferencing has become essential in modern business operations. However, varying internet speeds and device capabilities across users can lead to poor video quality and frustrating delays.
HEVC addresses these challenges by compressing video more efficiently, ensuring smoother communication with clearer visuals and less lag, even in bandwidth-constrained environments.
4. On-Camera Capture
HEVC isn’t just for distribution. Many high-resolution cameras, smartphones, and tablets record natively in H.265, so you can shoot 4K or 8K footage directly without losing detail.
Key Considerations When Implementing the HEVC Codec
After learning about the many advantages of using the HEVC (H.265) codec, you may be wondering what factors to consider before adopting it. Like any advanced technology, implementing HEVC comes with a few challenges. Fortunately, there are effective ways to address these considerations and ensure optimal performance.
1. Resource Demands
HEVC’s advanced compression capabilities come at the cost of increased computing power. Its sophisticated algorithms, designed to efficiently deliver high-quality video, require robust hardware and software.
To use HEVC effectively, your equipment, including cameras, encoding tools, and streaming platforms, must be high-performing. This may require businesses to invest in updated infrastructure.
However, the investment pays off. As 4K and 8K video become the industry standard, adopting HEVC is increasingly essential. Upgrading to compatible hardware and software ensures smooth performance and maximizes the codec’s benefits.
2. Encoding Complexity
Video encoding with HEVC can be more demanding than with older codecs due to its intricate compression processes. If your tools aren’t powerful or compatible enough, this can lead to encoding issues.
Businesses can mitigate these complications by ensuring their systems, both hardware and software, are designed to support HEVC. Using fully compatible and up-to-date technology reduces the likelihood of errors during encoding and helps maintain video quality and workflow efficiency.
3. Compatibility Challenges
Despite being introduced in 2003, the HEVC codec still presents compatibility hurdles due to its complex nature. Its powerful compression makes it effective, but also demands more from supporting devices and platforms.
While HEVC support is expanding rapidly, not all systems are fully compatible yet. Ensuring your tools, from video cameras to streaming platforms, support HEVC is key to a smooth implementation.
The good news: as technology evolves, more devices now support HEVC, and the codec is well on its way to becoming the norm. Many modern cameras and software solutions will explicitly state HEVC compatibility, making it easier to choose the right tools.
Optimize HEVC Video Files Automatically with Cloudinary
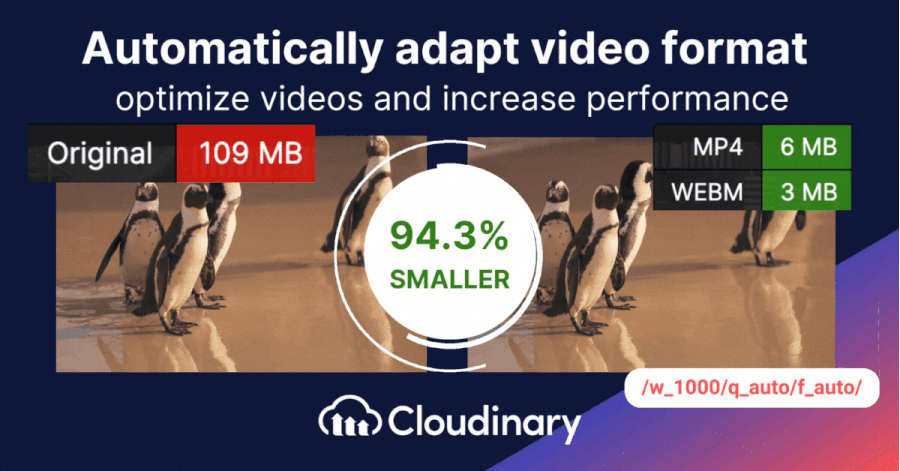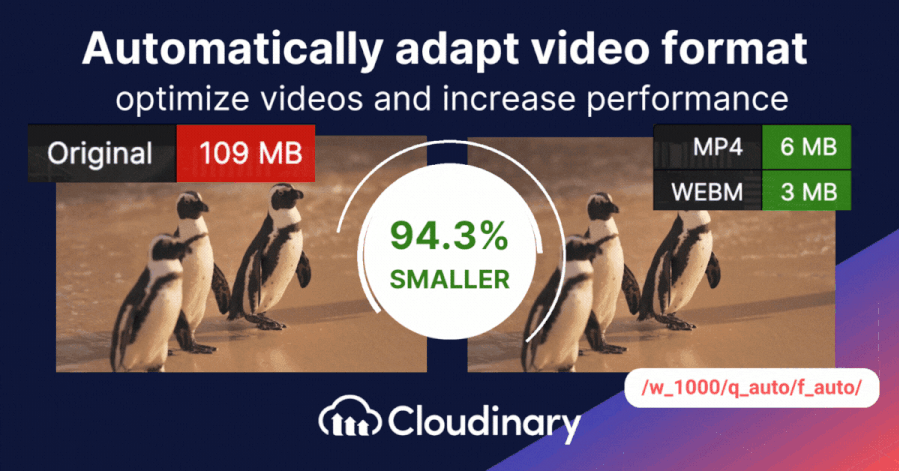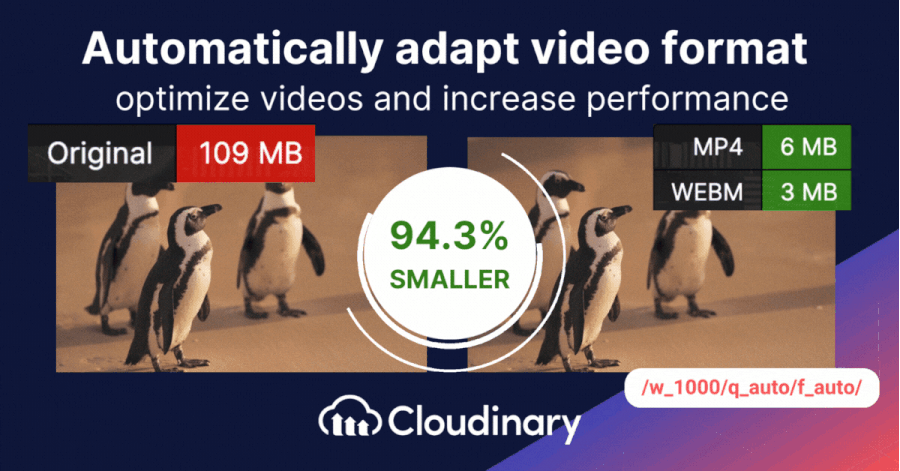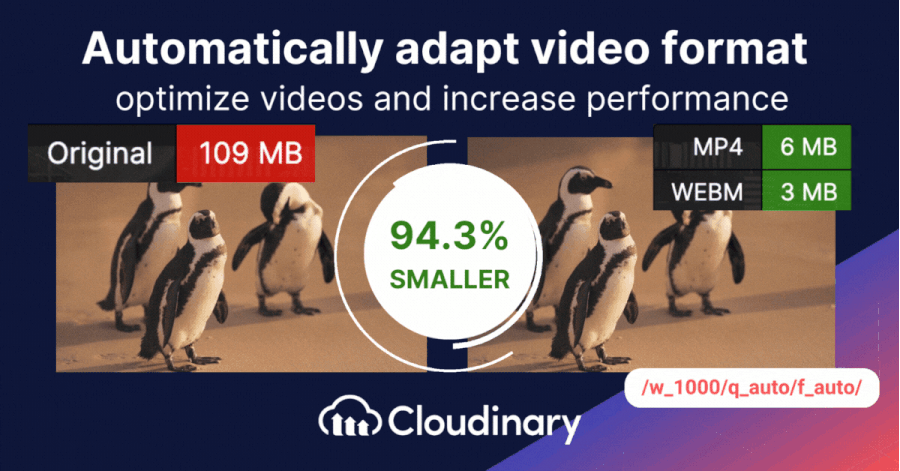
Storing and delivering video content can be challenging, especially when aiming for high quality without using too much bandwidth. That’s where Cloudinary steps in. Cloudinary presents two essential tools to enhance and deliver content more efficiently. These dynamic parameters ensure your videos are displayed at their best, adapting to diverse screen sizes and viewer preferences.
- Dynamic Quality Selection – q_auto: Cloudinary’s q_auto function stands out by autonomously determining the right equilibrium between video quality and file size. Whether you’re dealing with a basic clip or a big one, this tool adjusts accordingly. But if you prefer a hands-on approach, you can pinpoint the exact quality using q_auto:quality, substituting ‘quality’ with choices like ‘best’, ‘good’, ‘eco’, or ‘low’.
- Smart Video Resizing – w_1280,c_limit: This parameter is about delivering size-appropriate videos. Specifying the width (w), you guide Cloudinary to adjust your video’s width, using 1,280 pixels as an example here. If the original is narrower, there’s no overstretching; Cloudinary ensures it remains true to its original proportions. Though 1,280 pixels is a common benchmark, it fits your unique requirements.
Wrapping Up
Understanding video formats, HEVC being one among them, is crucial to make an informed decision. With its compression abilities, HEVC can help you deliver high-quality video without massive file sizes. Yet, as with any technology, there are considerations to weigh, especially when thinking about compatibility and the practical side of video editing and distribution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What file containers support HEVC?
HEVC bitstreams are typically wrapped in MP4 or MOV containers, which determine how video, audio, subtitles, and metadata are packaged. Your choice of container affects compatibility with players, support for closed-captions, and editing workflows.
Can I record in HEVC on my own device?
Yes. Most modern smartphones, tablets, and professional cameras let you record 4K (and sometimes 8K) video straight into HEVC. When you hit record, the device uses H.265 compression on the fly.
Which streaming services use HEVC today?
Leading platforms (like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, YouTube, and others) have rolled out HEVC-encoded streams for select titles, especially 4K/HDR content. By cutting their bitrate nearly in half versus H.264, they start playback faster and keep it smooth, even on constrained networks.