What Is MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP)?
MPEG-DASH (Dynamic Adaptive Streaming over HTTP) is an international standard for adaptive bitrate streaming that delivers high-quality video over regular HTTP servers. Like Apple’s HLS (HTTP Live Streaming), it breaks video content into small, time-segmented chunks that adjust dynamically to a viewer’s available bandwidth and device performance.
With MPEG-DASH, playback devices can switch between different bitrate versions of the same content in real time. This ensures smoother viewing experiences with fewer interruptions, especially during fluctuating network conditions.
How Does MPEG-DASH Work?
MPEG-DASH relies on Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR). A single video is encoded into multiple versions at different quality levels, which are then divided into short segments, typically lasting 2 to 4 seconds. As the video plays, the client device’s MPEG-DASH player (such as dash.js) selects and downloads the best-suited segment based on current bandwidth and CPU resources.
This dynamic adjustment helps prevent buffering and ensures viewers receive optimal quality, regardless of if they’re using a high-speed connection or mobile data.
Pro Tip
Consider Cloudinary’s Adaptive Bitrate Streaming
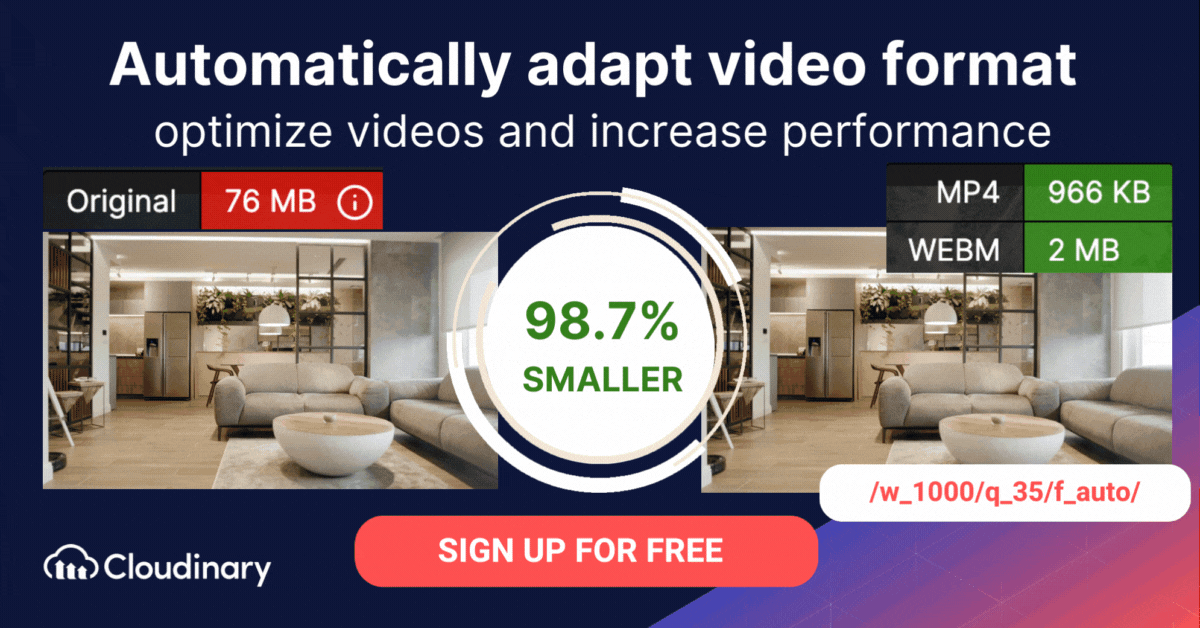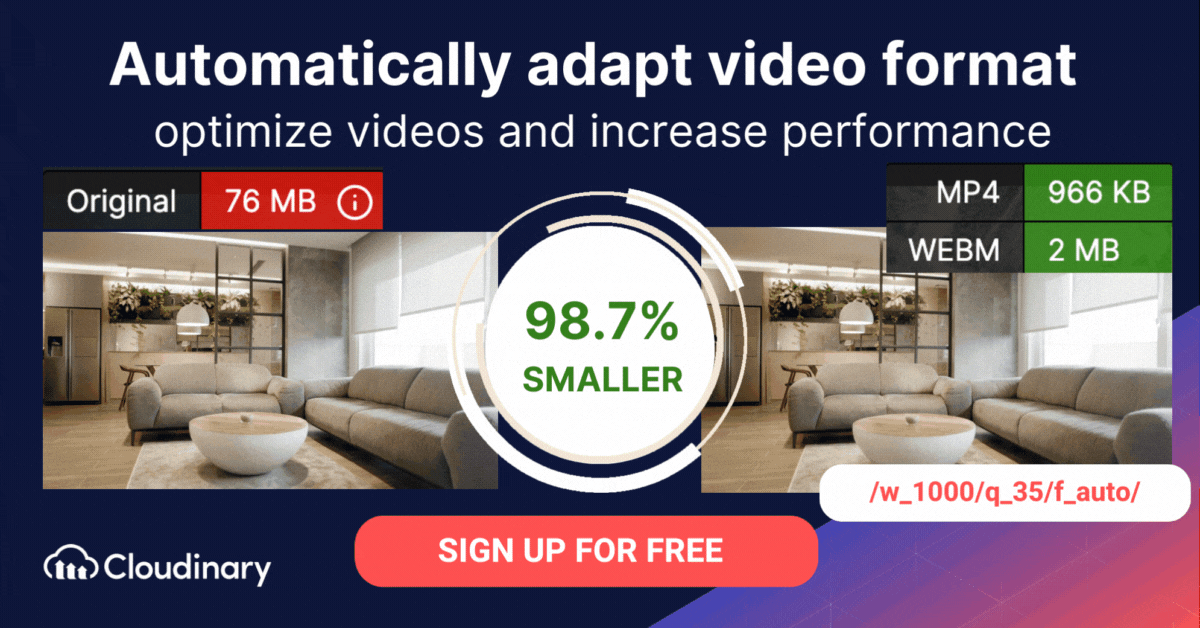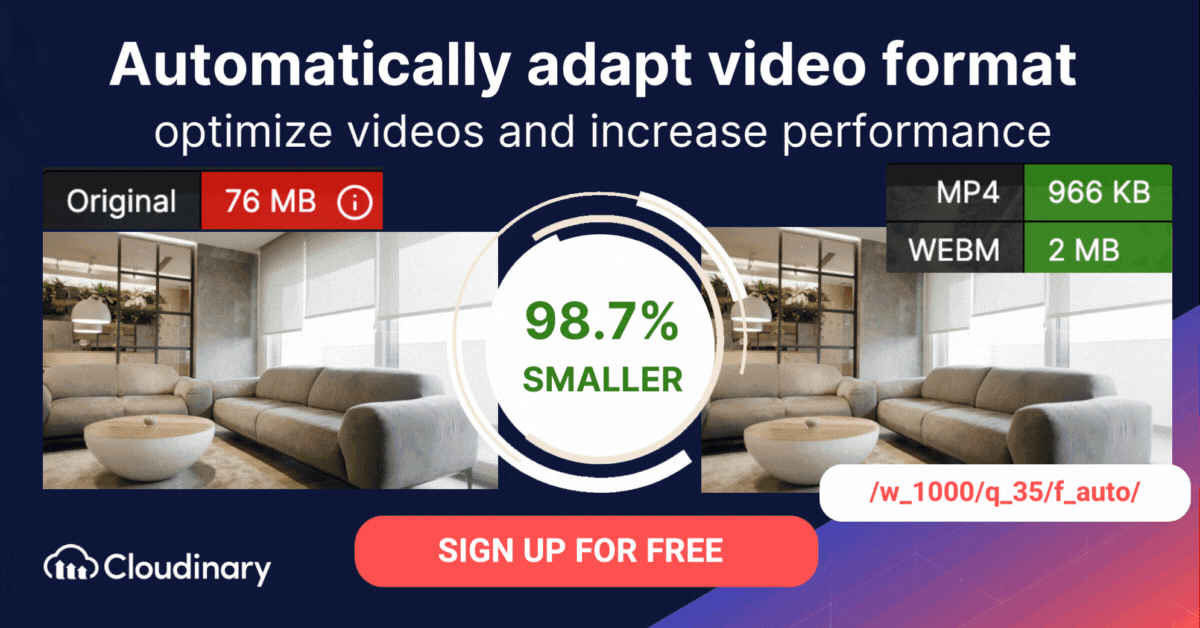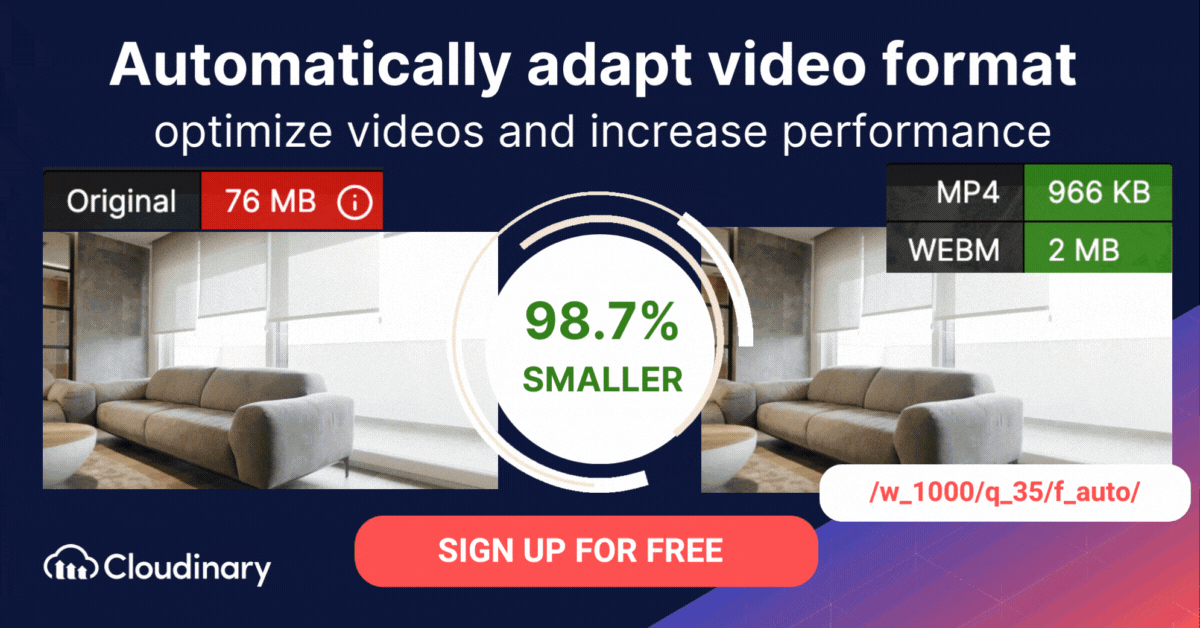
Adaptive bitrate streaming is a video delivery technique that adjusts the quality of a video stream in real time according to detected bandwidth and CPU capacity. This enables videos to start quicker, with fewer buffering interruptions, and at the best possible quality for the current device and network connection, to maximize user experience.
MPEG-DASH offers several key benefits for both developers and viewers. Its adaptive streaming capabilities allow video quality to adjust automatically based on the user’s network conditions, ensuring smooth playback without buffering interruptions.
As an open standard, MPEG-DASH supports a wide range of codecs, giving developers greater flexibility and making it easier to future-proof their media delivery pipelines. It also provides lower latency options, which is especially valuable for live streaming scenarios where real-time performance is critical. Additionally, MPEG-DASH is widely compatible with HTML5 video players such as Video.js, THEOplayer, Bitmovin, and VLC.
MPEG-DASH and Cloudinary
Cloudinary fully supports adaptive bitrate streaming with both MPEG-DASH and HLS, making it easy to deliver high-quality video tailored to each viewer’s network conditions and device. The platform automatically handles video transcoding and generates multiple renditions, ensuring smooth playback across bandwidth levels. It also creates MPEG-DASH manifest (MPD) files to streamline content delivery.
Videos can be embedded using Cloudinary’s customizable player or integrated into third-party players, offering flexibility in implementation. By managing the complexities of segmenting and encoding behind the scenes, Cloudinary allows developers to focus on creating seamless, scalable media experiences without the need for manual setup.