What Is AVI Format?
AVI, short for Audio Video Interleave, is a multimedia file format created by Microsoft in 1992 to combine audio and video into a single file. It allows synchronized playback of both components and is natively supported by all Microsoft Windows operating systems. AVI files can be opened using Windows Media Player and other compatible software.
The term “interleave” refers to the way audio and video data packets are alternated, or interleaved, in small chunks throughout the file to ensure smooth, synchronized playback without long buffering delays.
An audio video interleave file is based on the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF), a multimedia container format used to store multimedia data. They can store video and audio data encoded in various codecs, including DivX and XviD. The AVI file extension often uses the format extensions that Matrox OpenDML introduced in 1996. Microsoft supports these files, which are sometimes (unofficially) known as AVI 20.
AVI files are larger in size and may require compression to smaller file formats. In comparison, MP4 files are smaller in size and work with almost all media players, but have inferior video output quality. MP4 is the better file type for most use cases.
MOV is a video file format developed by Apple and serves as a modern alternative to AVI in many workflows. Based on the MPEG-4 standard, MOV supports multiple video tracks, audio streams, and even text, making it ideal for editing and advanced media applications. While AVI is still valued for its high video fidelity and reliable audio and video playback, especially for storage and archiving, MOV is typically favored in current editing environments because of its flexible codec support and high-quality output.
This is part of a series of articles about video format.
In this article:
- AVI RIFF File Structure
- What Is DV AVI?
- AVI File Format: Pros and Cons
- AVI vs MP4
- AVI vs MOV
- How Do You Convert AVI to MP4 Or WebM Format With Cloudinary?
How to Play an AVI File in Windows
To open an AVI file on Windows, you can:
- Double-click the video file.
- Right-click the file and select Windows Media Player from the “Open With” drop-down menu.
Windows Media Player provides basic functionality for AVI files, including playback control (pause, resume, stop), volume control, and a simple user interface to manage your media files.
AVI players for Windows include PlayerFab Ultra HD Player, DVDFab Player 5, VLC Player, KM Player, GOM Media Player, and RealPlayer. These players offer advanced features like subtitle support, enhanced playback controls, video and audio equalizers, multiple viewing modes, and compatibility with various media file types.
How to Play an AVI File on MacOS
Here’s how you can play AVI files on macOS:
Using VLC Media Player:
- Download and install VLC Media Player from the official website.
- Open VLC Media Player.
- Drag and drop the AVI file into the application, or use the “Open File” option.
While AVI files are playable on both Windows and macOS, MOV files, being Apple’s native format, provide seamless compatibility with macOS devices, including iMovie and Final Cut Pro. This makes MOV the better choice for Mac users who frequently edit videos.
AVI RIFF File Structure
The AVI format adheres to the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF) specification, which is used by applications that record, play, and edit video and audio sequences. AVI files usually contain multiple data streams, with video and audio being the most common. There is also a simpler version of the AVI format that includes only video data, excluding the audio stream.
A FOURCC (four-character code) is a 32-bit unsigned integer made up of four ASCII characters. It can include spaces, meaning a valid FOURCC can consist of three letters and a space. In the AVI format, FOURCCs are used to identify important details, such as stream types, data chunks, and index entries.
The structure of the AVI file format builds on the RIFF format used for documents. RIFF files consist of a header and (optionally) lists and data chunks.
RIFF headers typically have the form:
'RIFF' fileSize fileType (data)
In this context, RIFF refers to a FOURCC, the file size is a 4-byte value that indicates the size of the file’s data, and the file type is another FOURCC that identifies the file’s type. The file size includes the size of the file type FOURCC and the subsequent data, but does not account for the initial RIFF FOURCC or the file size component itself. The data consists of different lists and chunks, arranged in no particular order.
Chunks should use this form:
ckID ckSize ckData
The ckID component is a FOURCC that identifies the data within a chunk, while the ckSize component is a 4-byte value indicating the size of the chunk’s data. The chunk data (ckData) may contain any amount of data, including zero bytes. It is always padded to the nearest WORD boundary. The chunk size specifies the size of the valid data, excluding the padding and the ID and size components.
AVI lists follow this form:
'LIST' listSize listType listData
LIST is a FOURCC, while the 4-byte list size component specifies the list’s size. The list type component is another FOURCC, and the list data component includes lists or chunks in no particular order. The list size value includes list type and data size but not the LIST FOURCC or the list size component.
It is possible to include optional elements in the RIFF chunks by placing them in brackets.
Pro Tip!Video Transformations on the Fly
Cloudinary allows you to easily transform your videos on the fly to any required format, style and dimension, and apply effects and other visual enhancements. Supported formats include WMV, WebM, OGV, MXF, MPEG, MP4, among others.
What Codecs are Used with AVI Files?
The AVI format is codec-independent, meaning it can work with various codecs to compress and decompress video and audio data. A codec is a software tool that compresses data for faster transmission and decompresses it when received.
Some popular codecs used with AVI files include DivX, XviD, and MJPEG. DivX and XviD are both codecs that compress video data, allowing for smaller file sizes without a significant loss in quality. MJPEG, on the other hand, is a motion-JPEG codec, which is commonly used in video capture and editing applications.
It’s important to note that the same codec used to encode an AVI file must also be used to decode it. This means that if you want to play back an AVI file, you’ll need to have the right codec installed on the device. If you don’t, you may encounter errors or be unable to play the file.
What Is DV AVI?
A DV AVI file is an AVI with compressed video content that complies with the Digital Video (DV) standard. The two types of DV AVI files are:
- Type 1—an AVI file that keeps the multiplexed video and audio data stored together in the file’s video portion.
- Type 2—an AVI file that stores the audio data in a separate audio stream.
Ironically, the first type is the newer file type, but Microsoft chose to designate it as Type 1, while the older VfW-compatible version became Type 2. People often confuse these two file types because of the counterintuitive designations. From the late 1990s to the early 2000s, most professional-grade DV software and non-linear video editing programs only supported the Type 1 DV AVI format.
AVI File Format: Pros and Cons
Here are notable pros of the AVI file format:
- The AVI file format produces videos with high-quality audio fidelity.
- You can use AVI files to create playable discs and DVDs that store initial audio or video information.
- The AVI format includes compression capabilities ideal for promotions, advertising, and short films.
- Since Windows developed the AVI file format, it is playable on most Microsoft and non-Microsoft operating systems.
- There is no need to use specific hardware or software to run AVI files. This characteristic ensures many users can open videos distributed as AVI.
- AVI maintains high-quality master files, ensuring you can use these files to create various types of files.
Here are notable cons of the AVI file format:
- The original AVI specification does not allow encoding aspect ratio information. However, AVI 2.0 provides a standardized method for encoding this data.
- The different approaches to adding timecode to AVI files affect the format’s usability.
- Once you encode a video file in AVI, you cannot compress it with techniques requiring future frames data beyond the encoded B-frame.
- Using AVI files with variable bitrates (VBR) like MP3 audio is problematic at sample rates below 32 kHz.
- You need to hardcode subtitles into the video stream or distribute it in a separate file because the AVI files may not be able to accommodate attachments like subtitles and fonts.
- As a legacy format, AVI lacks many modern features (like built-in subtitles and streaming optimizations), making it less well suited for today’s online and mobile workflows.
AVI vs MP4
MP4 (MPEG-4 Part 14) is a format that stores video, audio, subtitles, and images in a single file. While AVI files are generally larger and may require compression, MP4 files are smaller and compatible with almost all media players. However, MP4 files may offer lower video quality compared to AVI. For most use cases, MP4 is the preferred format.
Let’s explore the differences between AVI and MP4 in more detail.
Quality
When comparing AVI to MP4 in terms of quality, you should consider that both formats are video wrappers. AVI is associated with the DivX codec, while MP4 uses the MPEG-4 AVC/H.264 codec. Another difference is that AVI can store an alpha channel, meaning the format can provide a higher-quality output file, while MP4 cannot. MP4, unlike AVI, can use different compression codecs, ensuring higher performance efficiency with comparable quality.
In the bottom line, there is no noticeable difference between AVI video and MP4 video. However, AVI provides slightly higher video quality than MP4.
Related content: Read our guide to video codecs
Storage efficiency
The AVI video format compresses data less efficiently than other video formats such as MP4, MPEG, and MOV. The result is a huge file size of 2-3 GB per minute of video on average. This is a problem for users with limited storage space. However, AVI files can be compressed by converting them to other formats such as MOV, FLV or MP4. MP4 is a lossy format that has strong compression capabilities and uses much less storage space than AVI.
Compatibility
MP4 has another key advantage over AVI—it is compatible with most devices, while AVI might require specialized players to run.
In the bottom line, for almost all use cases, you will find that MP4 is a superior format to AVI. If visual quality is the only consideration, you might prefer AVI over MP4.
Related content: Read about another modern video format in our guide to WebM Format
AVI vs MOV
MOV, on the other hand, is commonly used in professional editing environments because of its support for high-quality output and compatibility with advanced codecs. Unlike AVI, MOV files can manage multiple video and audio tracks, as well as text. This makes MOV perfect for complex projects that involve working with layered media.
When considering quality, both AVI and MOV provide excellent video fidelity, but MOV has the edge in flexibility and adaptability for modern applications. In contrast, AVI excels in archiving and storing media, as its simpler structure ensures compatibility across legacy systems.
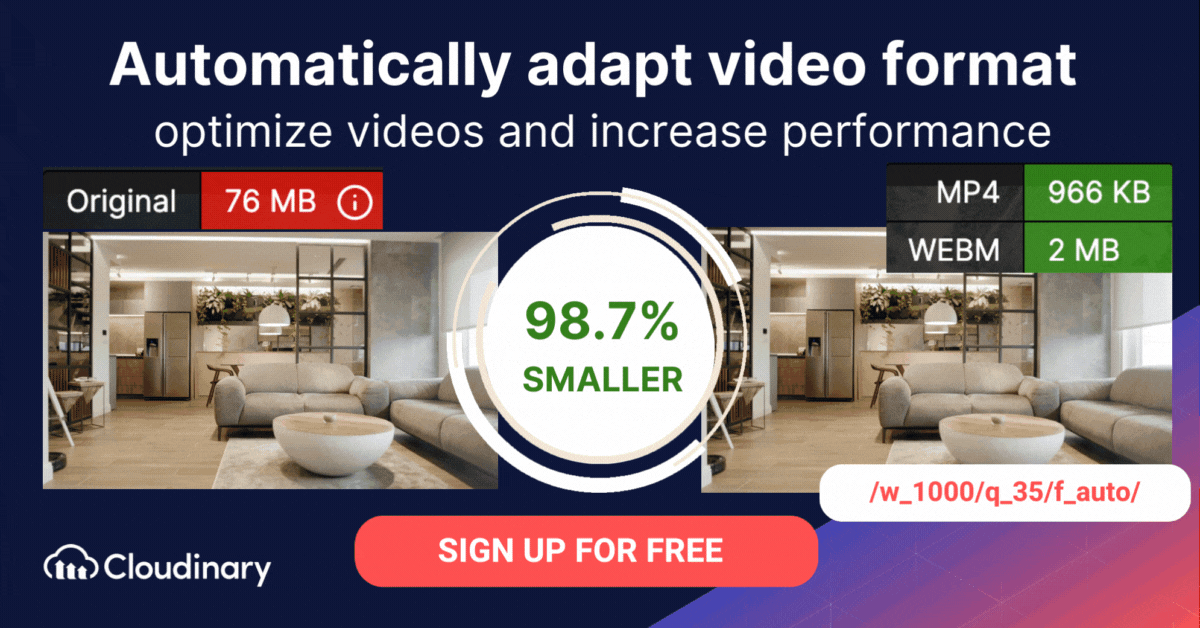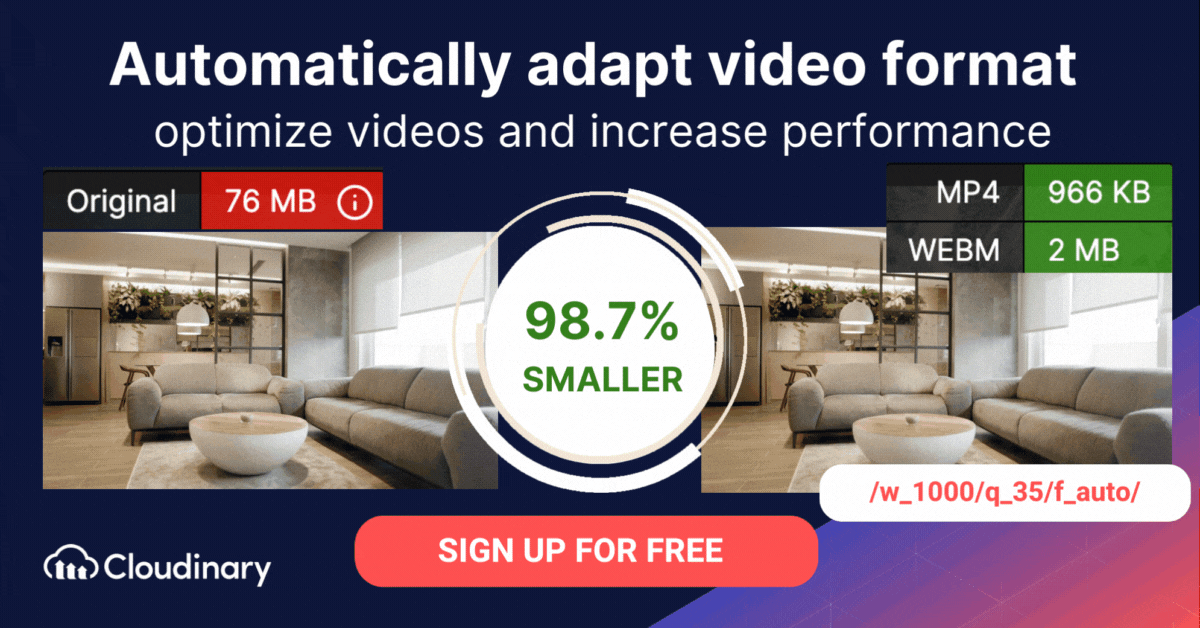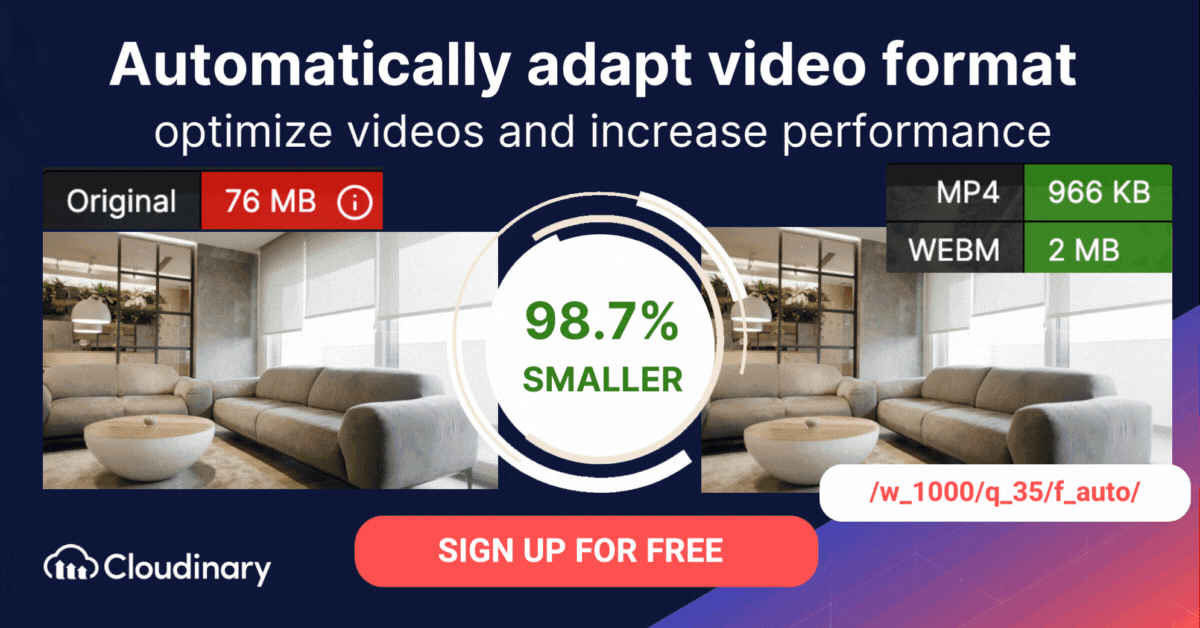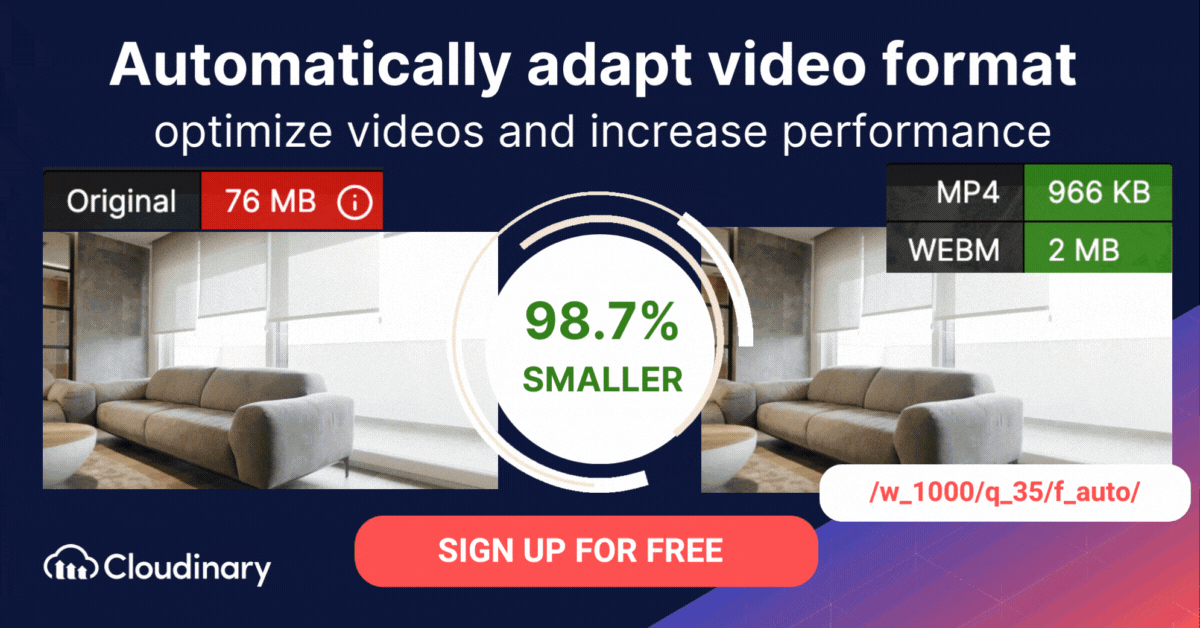
How Do You Convert AVI to MP4 Or WebM Format With Cloudinary?
The AVI format is typically less efficient than formats like MP4 and WebM. Cloudinary can assist in automatically converting AVI files to more modern video formats, ensuring faster loading times and an improved user experience.
Cloudinary performs the task in the cloud through automation in three steps:
- Convert AVI to MP4s or WebM through dynamic URLs.
- Resize, crop, and transform the videos generated in step 1.
- Optimize the transformed videos through a fast content delivery network (CDN).
The conversion capability is available in all Cloudinary plans, including the free tier. Do check it out.