What Is Video-Format Conversion?
Video-conversion tools convert one video format to another. A video-storage format depicts the structure of the video and usually specifies the encoding in use for video compression.
Video-conversion tools typically support numerous source and destination video formats, enabling the conversion of video or audio files from any of the source formats to any of the destination formats. In some cases, however, conversion might cause degradation in video quality.
This article covers the following topics:
- Why Do You Need Video-Format Conversion?
- How Do You Choose a Video Converter?
- Automated Video-Format Conversion with Cloudinary
Why Do You Need Video-Format Conversion?
Here are a few key reasons why you need to convert a video format to another.
Enabling Compatibility With Other Devices
Often, device-compatibility issues arise during file transfers from one device to another, likely because some devices or viewing platforms support only certain file types.
Digital cameras, for example, might save video files in a format that a mobile phone’s video player cannot read. A common strategy is to convert the video format to MP4, currently the most widely supported video format. For example, if a camera stores a video as a MOV file, convert it to an MP4 file to make it viewable on most devices. To view a video on an older 3G device, you might need to convert the video format to the .3GP format.
Converting Video Files to MP4
To further assist with device compatibility, here are detailed steps using specific software tools for converting video files to MP4:
Using a Dedicated MP4 Files Converter:
- Download, install, and launch the MP4 files converter.
- Click “Add Media” and choose “Add Video.”
- Select the files for conversion and click “Open.”
- Choose the appropriate output format.
- Click “Convert.”
Handbrake:
- Open Handbrake, a free video converter software.
- Click “Add Files” to select the original video.
- From the drop-down menu, select MP4 as the output format.
VLC Player:
- Open VLC Player.
- Go to the “Media” tab, and click “Convert/Save.”
- Click “Add” to select the video.
- Click “Convert/Save” again and select MP4 in the Profile drop-down menu.
Online Tools like Kapwing and VEED.IO:
- For Kapwing, upload a file, choose the export type, and share the converted video.
- For VEED.IO, select a file format, upload and convert the video, then download it.
These methods highlight the accessibility of video conversion for casual users, offering both desktop and online options.
Improving Compression
Most video formats compress data, reducing storage space. Another benefit is that compression enables videos to be viewed and streamed over the internet. However, different formats use different compression techniques, some of which are more efficient than others.
Most video formats use a video codec that defines the algorithm and parameters for compression. New codecs that support more efficient compression can reduce file size significantly. As a result, you might find yourself frequently converting video files to a newer format for a smaller file size.
Related content: A Primer on Video Codecs
Improving the Bitrate
Nowadays, people often publish video content online. However, each video-sharing platform has its own requirements and recommendations for videos. One such requirement is the bitrate, which is the number of bits transferred per second when a video is playing, i.e., a measure of the video file’s quality. A higher bitrate depicts higher quality, but higher bitrates result in larger files and slower buffering on online platforms.
Media platforms often recommend a range of suitable bitrates for videos of a particular resolution. Nonetheless, even if you publish your video on a platform that allows a high bitrate, it is usually a good idea to opt for a medium one so that viewers with slower connections can access the video quickly.
How Do You Choose a Video Convertor?
5 Essential Features of Video- Convertor Software
Many video conversion tools are available. Following are five evaluation criteria for them.
Number of Formats
Superior video-conversion tools offer many source and destination formats. The basic ones, such as MP4 and MOV, might not be suitable for all devices and scenarios.
In addition, tools like Handbrake and VLC Player are examples of software providing user-friendly options for casual users, often free and open-source. They offer a straightforward way to convert file types into popular formats like MP4.
In addition, first-rate conversion tools support optimized, next-generation formats like WebM. Some conversion tools are easy to use with limited options; others need extensive configurations. Select a tool that matches your level of expertise.
Video Quality
Quality degradation as a result of video conversion is a common occurrence. To minimize loss of quality, start with a high-quality video file and maintain approximately the same resolution as the original. A good conversion tool would automatically suggest the best options for your target video format and warn you against options that do not make sense—for example, converting a lossy format to a lossless one.
Support for Operating System
Before choosing a video converter, ensure that it is compatible with your operating system. Also consider if you intend to edit and convert videos on a desktop computer, a mobile device, or another type of device. Some video-conversion tools are explicitly designed for desktop devices, mobile devices, or both.
Conversion Speed
Video files are large, and converting their formats might take a long time, depending on your device’s computing power. Some video-conversion tools have optimized algorithms that can convert files faster so, if you have a large volume of files to convert, pay attention to the conversion speed.
Batch Processing
For converting more than just an occasional video, batch-conversion options might come in handy. With those options, you can select multiple video files or an entire folder, define a destination video format, and have the video converter process them automatically.
Subtitles and Video Editing
Advanced video conversion tools can do more than convert video as-is between formats, e.g., you can add subtitles, resize or crop your video, and transpose images or text. Many video-editing tools are also video-conversion tools because they support a variety of video formats.
Automated Video-Format Conversion With Cloudinary
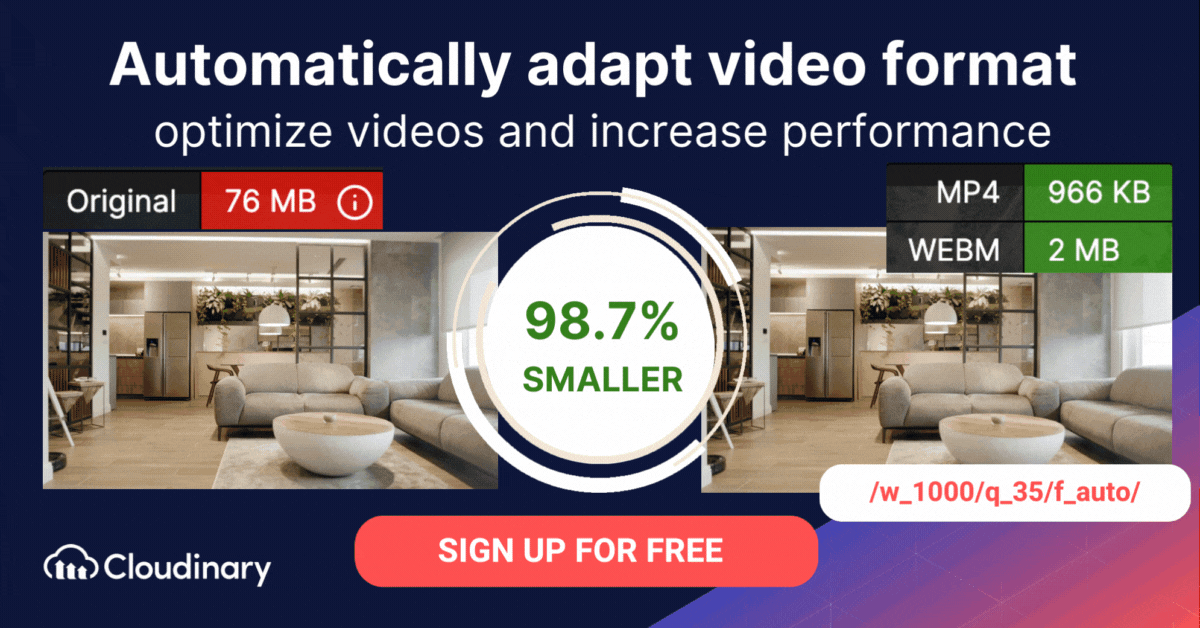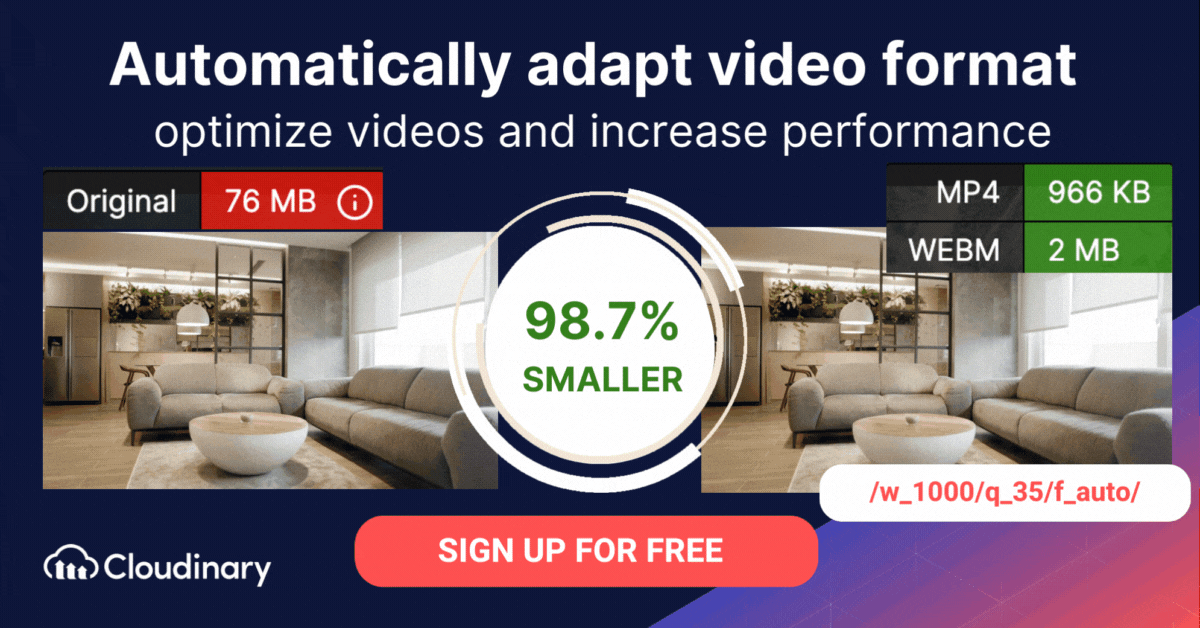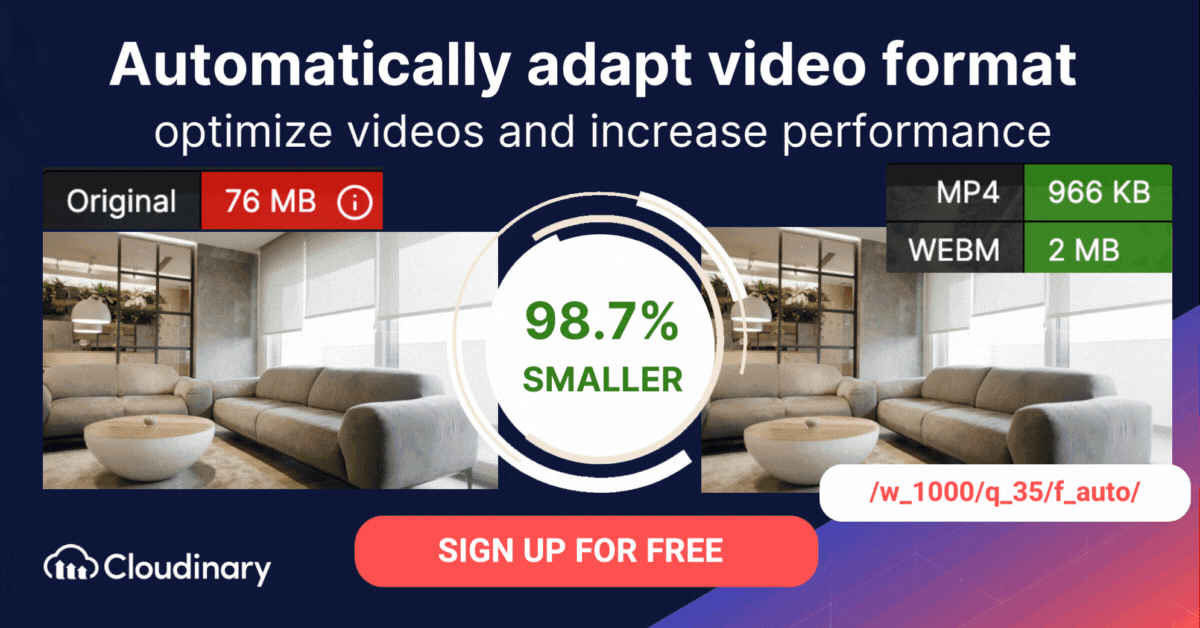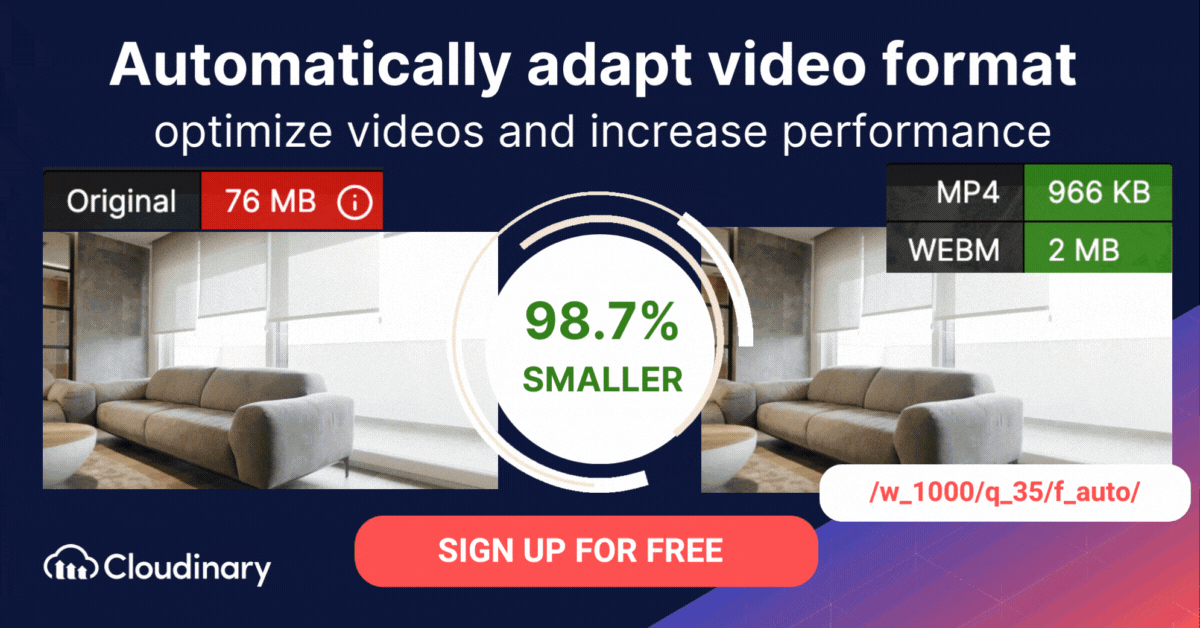
Cloudinary offers a versatile, effective, and efficient solution for managing media, replete with dynamic, automated optimization and delivery features. For example, setting the fetch_format parameter to auto (f_auto in URLs) causes Cloudinary to automatically select the format and codec based on the requesting browser. Chrome users would most likely receive a VP9-encoded WebM file; Safari users, an HEVC-encoded MP4 file. If a browser does not support either of those formats, Cloudinary delivers the video as an H.264-encoded MP4 file, which works in almost all browsers.
Interested? Have a try for free by first signing up for a free Cloudinary account.