What Is the WMV Format?
WMV stands for Windows Media Video. The WMV format is a compressed video container format developed by Microsoft. WMV files can store animations, video clips, TV episodes, or movies. They can be used for online video streaming and sharing video content via HD DVD and Blu-ray Discs.
WMV files are saved in the Microsoft Advanced Systems Format (ASF) and compressed with WMV compression. This video format supports high-definition (HD) video and encryption for digital rights management (DRM) systems. It provides three variants (codecs) called ‘Video’, ‘Image’ and ‘Screen’.
Software that can play WMV files includes:
- Windows Media Player
- VLC Media Player
- RealPlayer
- MPlayer
- Media Player Classic
You can convert WMV files to MP4 and other popular formats using Cloudinary, a cloud-based media management platform.
Related content: Read our guide to video codecs
In this article:
- History of WMV
- Other Formats Supported on Windows
- WMV File Format Specifications
- Windows Media Video Format Variants
- WMV Format Pros and Cons
- How Do You Convert WMV to MP4 Or WebM Format With Cloudinary?
History of WMV
Microsoft introduced the WMV Video, Screen, and Image codec in 1999 as part of the Windows Media framework. Since then, it has become a popular codec, widely used to compress and convert ASF videos to WMV files. You can play WMV on various media players, Windows and otherwise, and stream it over the Internet.
The first version, VMV 7, was based on MPEG-4 Part 2. Microsoft continued development of the format, and its proprietary bit stream syntax was frozen in WMV 9. This version introduced several important features including:
- Native support for interlaced video
- Non-square pixels
- Frame interpolation
- A profile called Windows Media Video 9 Professional which is used automatically when resolution exceeds 300K pixels and bitrate exceeds 1000 kbit/sec.
Other Formats Supported on Windows
In addition to WMV, Windows systems and Windows Media Player natively support several other popular container formats (like AVI, MP4, and MPEG‑1/MPEG‑2) without requiring extra installations. For less common formats (such as MKV, MOV, or TS), users often need to install codec packs or rely on third‑party players that bundle broader codec libraries. This distinction between container (the file wrapper, like AVI or MKV) and codec (the compression algorithm inside, like H.264 or WMV) is key: playback issues usually stem from missing codecs rather than unsupported file extensions.
WMV File Format Specifications
The WMV format is usually packed into ASF containers, but Matroska and AVI containers also support WMV with the .mkv and .avi extensions. WMV-9 is the latest, best codec available in Windows Media Video, offering low bit-rate compression. It has an 8-bit 4:2:0 color format and uses block-based spatial transformation and motion compensation.
WMV uses a motion vector to help compensate for motion between frames. It forms each block by predicting values based on preceding reconstructed frames, calculating the residual error between the actual and predicted block. A linear quantized, entropy-encoded transform is used to transform the residual error (which the decoder side then decodes and de-quantizes).
WMV 9 has three types of frames: intra I frames (independently coded); predicted P frames (dependent on a previous frame); bi-directionally predicted B frames (with references in the past and future). WMV-9 does not use the bi-directional (B) frames as references for other frames, so they remain outside the decoding loop.
Windows Media Video Format Variants
In addition to the basic WMV format, known as the Video codec, there are two additional variants of the format designed for special use cases: WMV Screen and WMV Image.
WMV Screen Codec
The Windows Media Video 9 Screen codec is designed for screenshots of applications intended to be shown on a computer display. For example, it can be used to transmit screen images when remotely accessing computer systems.
This codec assumes that a screen image is relatively simple, with fewer colors, more straight lines, and less motion than typical video content. It uses these characteristics to achieve very high compression compared to the WMV Video codec.
WMV Image Codec
Windows Media Video Image is a slideshow format, which contains a series of images and applies effects like timing, panning, and transitions during playback. For still images combined into a slideshow, it can achieve higher compression than the WMV 9 Video codec. A new version of the format, WMV 9.1 Image, supports more transformation effects between slides, but is not backward compatible.
A downside of this format is that it requires the player to generate video frames in real-time. Playing WMV Image files at moderate resolution, for example 1024×768 with 30 fps, requires a large amount of processing power.
How Can You Play WMV Files?
Playing WMV files is relatively straightforward, especially if you are using a Windows system. Below are some common methods to play WMV files:
Using Native Software on Windows
- Windows Media Player: On a Windows System, double-clicking the WMV file will usually open the file in Windows Media Player. You can also right-click the file, choose Open with, and select Windows Media Player.
- Microsoft Movies & TV: This is another native Windows application that can play WMV files. Simply right-click the WMV file and choose Open with > Movies & TV
- Clipchamp (Windows 11): Microsoft’s free video editor that can also import and play WMV files (and export to other formats). It’s useful for quick edits, trimming, and basic transitions without needing separate software.
Using Third-Party Software
- VLC Media Player: This is a free, open-source media player that can handle almost any type of video file, including WMV. Download and install VLC, and then open the application. Drag and drop the WMV file into VLC, or go to Media > Open File and navigate to your WMV file.
- RealPlayer: After installing RealPlayer, you can open it and drag your WMV file into the media library, or use the File > Open menu to find your WMV file.
- MPlayer or Media Player Classic: These are additional options for playing WMV files. Simply download and install the program, then use the File menu to open your WMV file.
On Mac
- Flip4Mac WMV Components for QuickTime: This is an optional component for QuickTime that allows WMV playback on Mac systems.
- VLC for Mac: The Mac version of VLC Media Player can also play WMV files.
On Linux
- VLC for Linux: VLC is also available for Linux systems and can play WMV files.
- MPlayer for Linux: This is another media player for Linux that supports WMV files.
On Mobile Devices
- VLC for Android and iOS: The mobile versions of VLC can also handle WMV files.
Dedicated Apps: There are various dedicated apps available on Android and iOS platforms that can play WMV files. However, the compatibility and functionality can vary.
Pro Tip!
Effortlessly Convert Your Videos.
Cloudinary lets you effortlessly convert videos to any necessary format without the need for software or coding skills. Just upload your video and deliver it in any required format through a URL, applying effects and other visual enhancements as needed.
WMV Format Pros and Cons
Here are the main advantages of using the WMV format:
- The WMV format keeps a large quantity of audio and video data in smaller storage spaces, making it ideal for streaming videos over the Internet.
- The WMV format is the default format in several Windows devices and is compatible with all Windows devices.
- Many legacy applications, including older versions of PowerPoint, support the WMV format.
- WMV offers a 2x compression ratio compared to MPEG-4.
- It is one of the smallest video formats, ideal for email attachments.
- You can use Google Drive to make the format available online.
- You can use it with many converters.
Here are the main disadvantages of using the WMV format:
- The WMV format is proprietary to Microsoft and not compatible with other operating systems. However, there are Apple-based and Linux media players that can run WMV files, such as Apple’s Flip4Mac WMV QuickTime component.
- All WMV files use a digital rights management system. These systems, particularly Windows Media Player 11, often make it impossible to restore the licensing information attached to WMV files.
- Not all applications are designed to work with the small file size produced by the WMV format.
- The term WMV refers to the file container format as well as the Windows Media Video codec. As a result, it can be difficult to determine whether a WMV file contains compression by other supported codecs.
What are the differences between MP4 and WMV?
Understanding the world of digital media formats can seem complex given the array of options. MP4 and WMV are two such formats, each with its own distinct characteristics. Throughout the digital media landscape, these two formats have established their prominence. But how do they differ? Let’s dissect the features of these media formats for more clarity.
- Encoding Method – MP4 and WMV use different encoding methods. MP4 employs H.264 or H.265 encoded video content along with AAC-encoded audio content. On the other hand, WMV uses Advanced Systems Format (ASF) as its container format. While the WMV encoding process generally compresses videos more, it’s worth mentioning that MP4 videos tend to preserve more quality.
- Popularity – Both MP4 and WMV have managed to carve out their own niches of popularity. However, MP4 edges out as the more popular format as it’s seen as an industry-wide standard compatible with almost all platforms. WMV, while not as universally accepted, is generally popular with Windows users. It’s worth noting that with the right plugin, WMV files can work on most platforms.
- Compatibility – The compatibility between the two formats can be quite stark depending on the platforms being used. If you require maximum compatibility across diverse platforms or if you’re a Mac user, MP4 takes the lead as it eliminates the need for further plugins. On the flipside, for dedicated Windows users, WMV might seamlessly cater to their needs without external complications.
- Video Quality – MP4 and WMV prove their individual strengths when it comes down to video quality. While in general, MP4 is accepted to have superior video quality, it’s essential to note that the video’s encoding and original source also play pivotal roles. Hence, a WMV file may produce a better quality video if the source is high quality.
- File Size – The last differential factor in the MP4 vs. WMV debate boils down to file size. If all factors such as video length and resolution remain constant, MP4 files are typically heftier than their WMV counterparts. If memory space is a priority, WMV files with their compressed format provide crunched down video files that are easier to store.
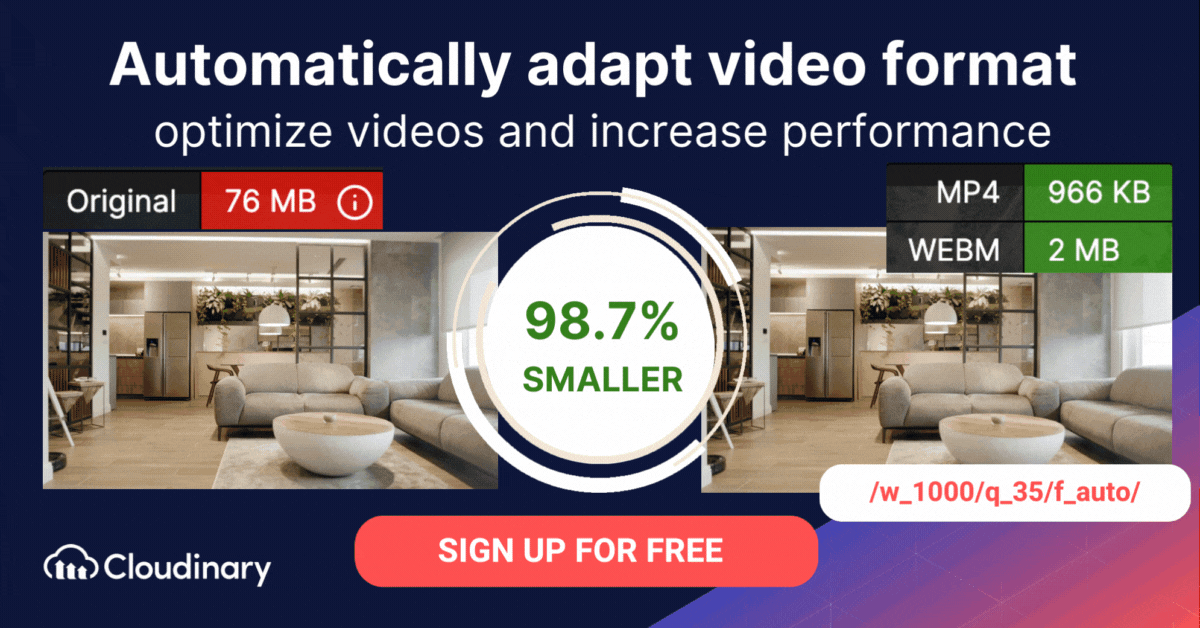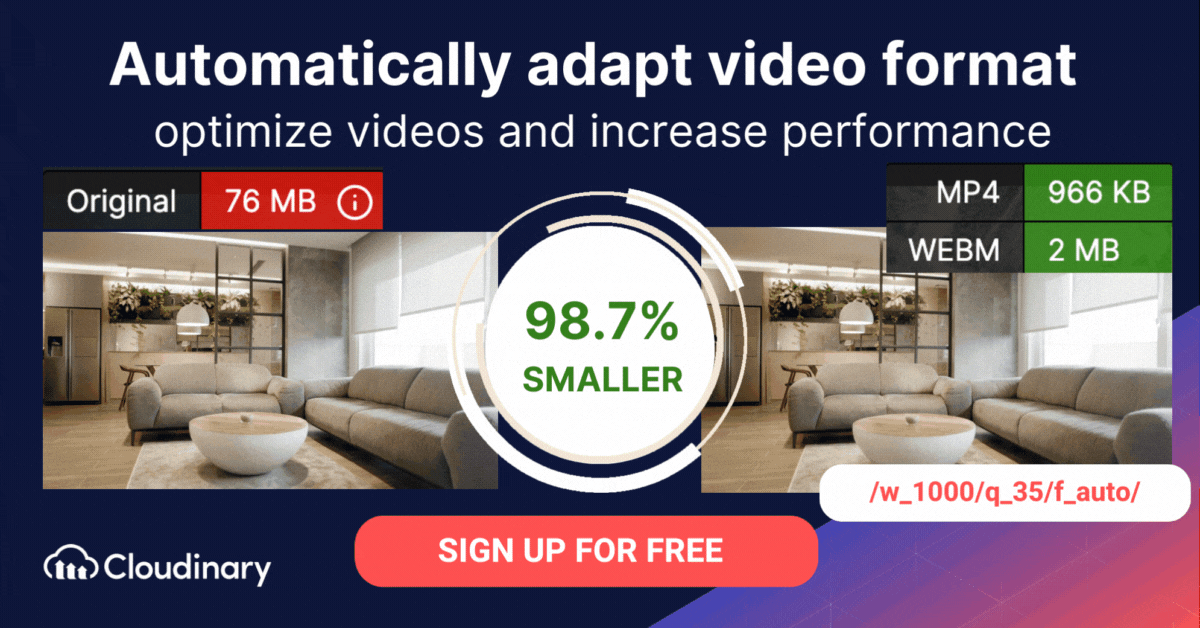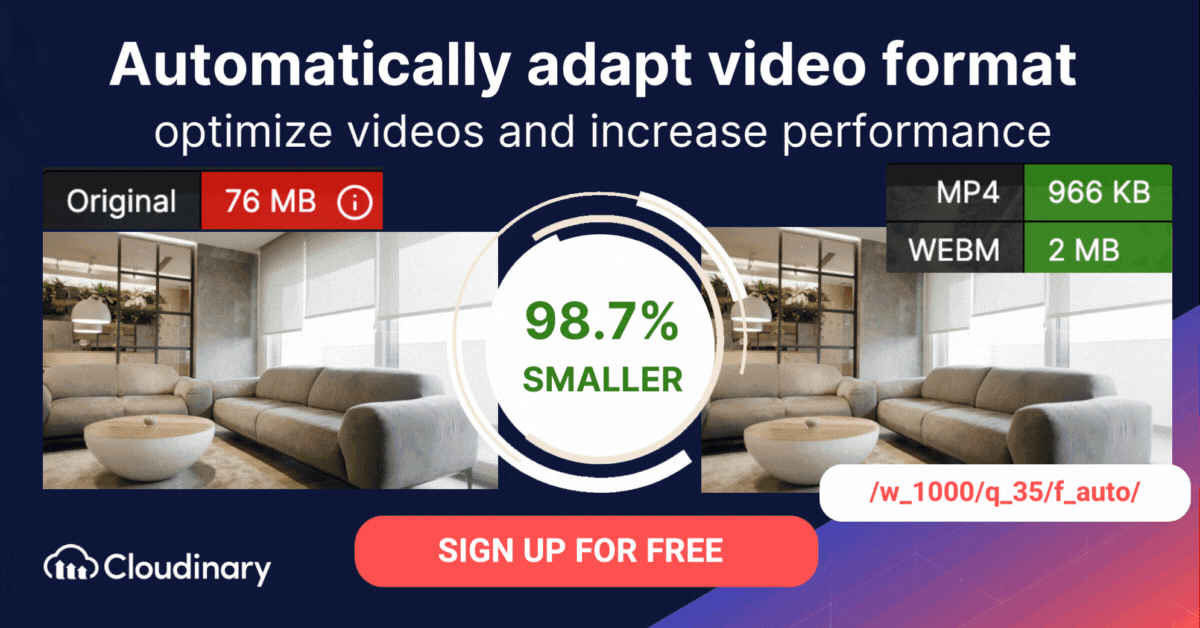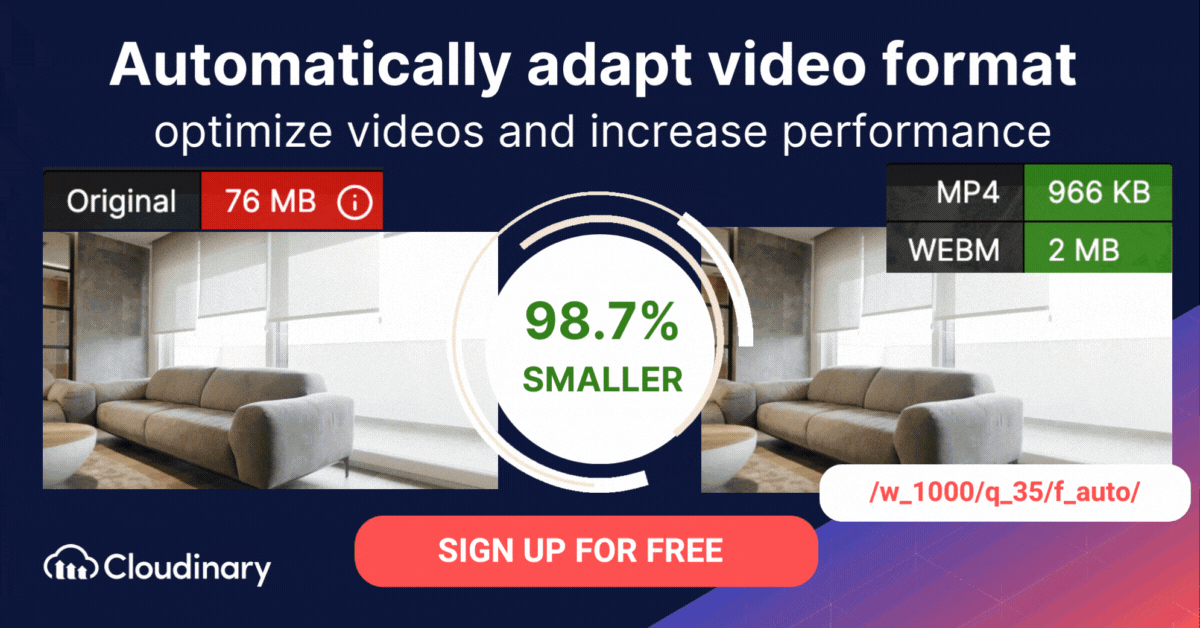
How Do You Convert WMV to MP4 or WebM Format with Cloudinary?
The WMV format is proprietary to Microsoft and is not compatible with many devices and applications. Cloudinary can help you automatically convert M4V files to modern video formats for faster loading, and an enhanced user experience.
Cloudinary performs the task in the cloud through automation in three steps:
- Convert M4V to MP4s or WebM through dynamic URLs.
- Resize, crop, and transform the videos generated in step 1.
- Optimize the transformed videos through a fast content delivery network (CDN).
The conversion capability is available in all Cloudinary plans, including the free tier. Do check it out.