What Is Content Scraping?
Content scraping, also known as data extraction or web scraping, is the process of extracting information from a website. Humans or computers can do this, taking place manually or automatically. Content scraping is performed using specialized software tools, custom-built scripts, or browser extensions that automate data extraction.
While content scraping can have legitimate uses, such as market research, data analysis, and content aggregation, it can also be employed unethically to steal copyrighted material or intellectual property. As a result, website owners should be aware of the potential risks associated with content scraping and take necessary precautions to protect their valuable digital assets. This may include implementing security measures, such as CAPTCHAs, rate limiting, or user authentication, to deter unauthorized access and data extraction.
Types of Content Targeted by Scrapers
It’s important to note that while content scraping can be used for legitimate purposes, such as data analysis and market research, it can also be employed unethically to steal copyrighted material or intellectual property. As a result, website owners must be vigilant in protecting their digital assets and implementing necessary security measures to deter unauthorized access and data extraction.
One of the most common types of content targeted by scrapers is anything not protected by robots.txt, which allows you to specify how search engines should interact with your website. As such, most scrapers will aim to pull information from websites that don’t use robots.txt or have it set up incorrectly.
Another popular tactic is targeting pages that have already been indexed in search engines but are no longer being crawled regularly (or ever). However, they still contain valuable information that can be used in other contexts – for example, if a person wants to find out about something like HTML5 video coding but doesn’t know where else besides Wikipedia would be reliable enough for such an endeavor.
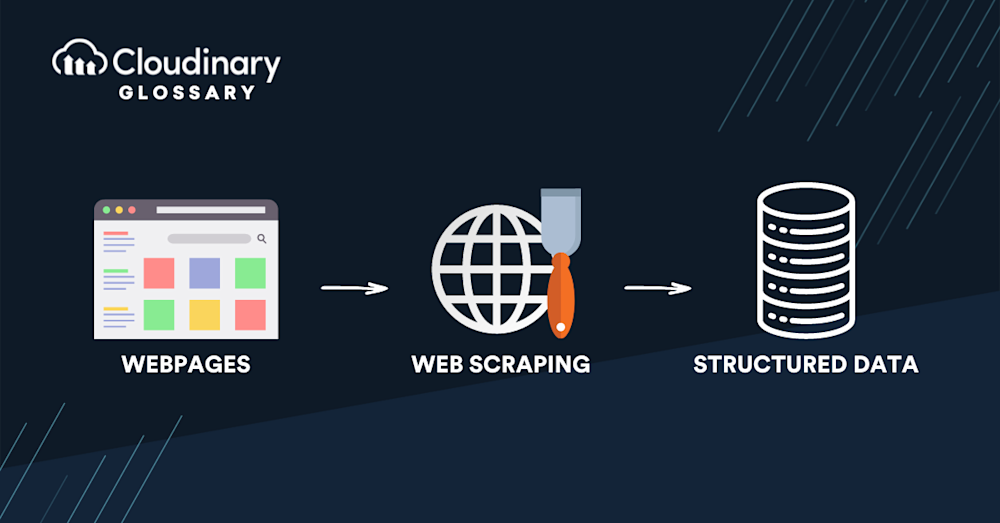
How Do Bots Scrape Content?
Bots play a significant role in the content scraping process. These bots are programmed to navigate websites, identify and access specific content, and extract the desired information. They operate by sending HTTP requests to web servers, just like a human user browsing the internet, but at a much faster pace and with the ability to process large amounts of data in a short amount of time.
To scrape content, bots typically follow a series of steps. First, they access the target website’s URL and download the HTML source code. Next, they parse the HTML code to identify the desired information elements, such as headings, paragraphs, or images. Once the relevant content is located, the bot extracts the data and stores it in a structured format, such as a spreadsheet or database, for further analysis.
Conclusion
Content scraping is a prevalent practice in the digital world, with both legitimate and unethical applications. As a website owner or developer, it’s essential to understand the potential risks associated with content scraping and take the necessary steps to protect your valuable digital assets from unauthorized access and data extraction.
One way to safeguard your content is by investing in a robust Digital Asset Management (DAM) solution, like Cloudinary. With advanced features such as metadata tagging, version control, and powerful search capabilities, Cloudinary helps you efficiently manage, store, and share your media assets while maintaining control over their usage. Don’t let content scraping compromise your hard work and intellectual property.
Sign up for Cloudinary today and experience the best DAM solution to protect and optimize your digital content.
Check Out Our Tools That You May Find Useful:


