What Is a CDN Edge Server?
A CDN Edge Server is a key component of a Content Delivery Network (CDN) strategically stationed at the network’s edge, closer to end-users. It acts as a caching server that stores and delivers content to users from the nearest possible location, ensuring optimal performance, minimized latency, and enhanced user experience.
The role of CDN Edge Servers is more than spanning distances; they also help absorb and mitigate traffic spikes, secure data transfers, and ensure high availability during peak times or unforeseen outages. Through caching strategies, they store static content (the parts of a website that don’t change often) and, in some advanced configurations, can even process dynamic content tailored to individual user requests.
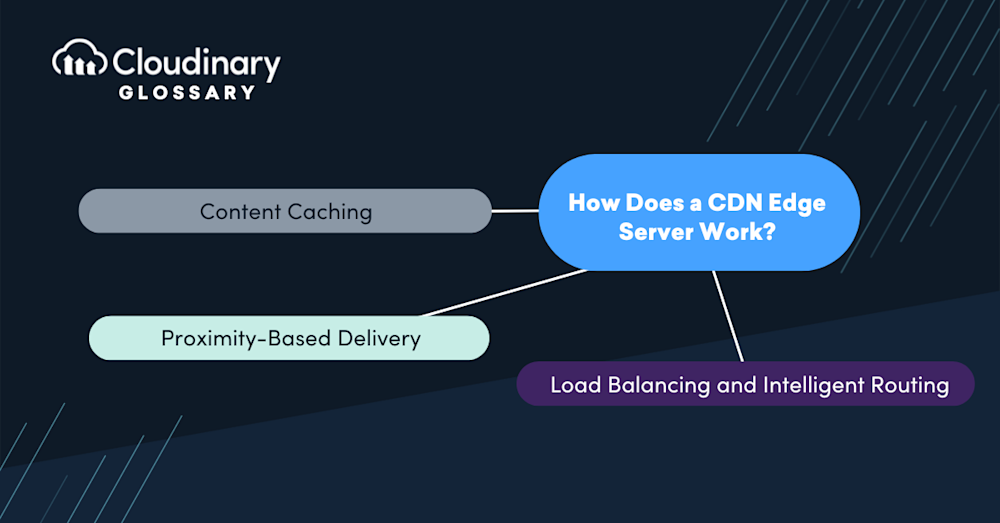
How Does a CDN Edge Server Work?
CDN edge servers work in conjunction with the overall CDN infrastructure to deliver content efficiently. The process can be summarized as follows:
- Content Caching – CDN providers deploy numerous edge server locations globally. When a user requests content, such as images, videos, or web pages, the CDN edge server closest to the user’s location responds to the request. It fetches the content from the origin server, which could be the customer’s server or a central content repository, and caches it on the edge server.
- Proximity-Based Delivery—With content cached on the edge server, subsequent requests for the same content from nearby users can be served directly from the edge server. By CDN edge servers enable faster content delivery by reducing the round-trip time and minimizing network latency, as the data does not need to traverse long distances.
- Load Balancing and Intelligent Routing – CDN providers employ smart algorithms to intelligently route user requests to the nearest available edge server. This ensures load distribution across multiple edge servers, optimizing performance and ensuring high availability.
CDN Edge Servers vs. Edge Servers
At first glance, these terms might seem interchangeable due to their focus on delivering content from closer physical proximity to the end-user. However, understanding the nuances and roles of each reveals a more comprehensive picture that helps make informed decisions in the tech landscape.
CDN Edge Servers are integral components of a Content Delivery Network (CDN), strategically placed in various locations worldwide to cache static content from the origin server. This means that when a user requests a webpage or media file, the request is routed to the closest CDN edge server, significantly reducing latency, improving load times, and diminishing the bandwidth load on the origin server.
On the other hand, Edge Servers, a broader classification, refer to any server that acts as an intermediary between the user and the core network or main data center. While CDN edge servers focus primarily on caching and delivering static content quickly, edge servers can perform a variety of tasks, including load balancing, security functions, and localized processing. Essentially, while all CDN edge servers can be considered edge servers, not all edge servers function as part of a CDN.
Where Are CDN Edge Servers Used?
CDN edge servers have a wide range of applications and are used in various scenarios, including:
- Website Delivery – CDN edge servers are extensively used to deliver web content, such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and media files, to users around the world. By caching and serving content from edge servers closer to the users, website owners can provide fast and reliable access to their web pages.
- Video Streaming – CDN edge servers play a crucial role in streaming platforms by distributing video content efficiently. With edge servers located in various geographical regions, video streaming providers can deliver high-quality video streams with minimized buffering and latency, regardless of the user’s location.
- Software Download – CDN edge servers are leveraged to distribute software downloads, ranging from small applications to large installation files. By caching the files on edge servers, software providers can accelerate the download process and handle high traffic loads efficiently.
- Gaming – The gaming industry heavily relies on CDN edge servers to deliver game updates, patches, and downloadable content (DLC) to gamers worldwide. By caching game files on edge servers, updates can be delivered quickly, reducing download times and enhancing the gaming experience.
Final Thoughts
CDN edge servers are the unsung heroes behind the seamless and speedy delivery of online content. By caching and serving content from strategically located servers, CDN edge servers minimize latency, optimize performance, and enhance user experience.
To take advantage of the benefits offered by CDN edge servers seamlessly, consider leveraging Cloudinary, a leading cloud-based media management platform. With its global network of CDN edge servers, and advanced content delivery solutions, Cloudinary ensures rapid and reliable content delivery to end-users, regardless of their location.
Simplify your digital asset delivery with Cloudinary’s fast and secure CDN integration. Sign up for free today!