Image accessibility
Last updated: Dec-23-2025
Making images accessible to all users, including those using assistive technologies, is essential for creating inclusive digital experiences. This guide covers best practices for implementing text alternatives, managing accessibility metadata at scale with Cloudinary's asset management tools, and leveraging AI-powered solutions to automatically generate descriptive content for your image library.
Image accessibility considerations
| Consideration | Cloudinary Image Techniques | WCAG Reference |
|---|---|---|
|
Consider how users with visual impairments will understand your images. They may rely on screen readers that need descriptive text alternatives to convey the same information. |
🔧 Managing text alternatives 🔧 AI-based image captioning 🔧 Cloudinary AI Vision |
1.1.1 Non-text content |
Text alternatives
Text alternatives are crucial for making visual content accessible to everyone, particularly users with visual impairments, cognitive disabilities, or those using assistive technologies like screen readers. These alternatives provide equivalent information about images, charts, diagrams, and other visual content in a format that can be understood through text-to-speech software, braille displays, or simply read by users who prefer textual descriptions.
Text alternatives can be used in:
-
Alt text (alternative text): The most common form of text alternative, typically provided through the
altattribute in HTML image tags. Alt text should be concise and descriptive, focusing on the essential information the image conveys. - Extended descriptions: For complex images like charts, diagrams, or infographics that require more detailed explanation than alt text can provide.
- Captions and figcaptions: Visible text that appears alongside images, providing context or description that benefits all users, not just those using assistive technology.
-
ARIA labels: Using
aria-label,aria-labelledby, oraria-describedbyattributes to provide accessible labels for interactive elements or complex visual content.
Good alt text should be:
- Concise but descriptive: Aim for one to two sentences that capture the essential information
- Context-appropriate: Consider how the image relates to surrounding content
- Functional: Describe what the image does or represents, not just what it looks like
- Equivalent: Provide the same information the image would convey to a sighted user
-
Relevant: Use empty alt text (
alt="") for purely decorative images that don't convey meaningful information
Cloudinary provides tools and approaches for managing text alternatives at scale, including:
- Centralized metadata management: Store alt text and descriptions with your assets as the single source of truth
- AI-powered generation: Automatically generate descriptive alt text using machine learning
Managing text alternatives
Cloudinary Assets, Cloudinary's Digital Asset Management (DAM) product, serves as the single source of truth for managing text alternatives across your entire Media Library. Rather than maintaining alt text in multiple locations throughout your application, you can centralize all accessibility metadata within Cloudinary Assets, enabling consistent management, review, and approval workflows.
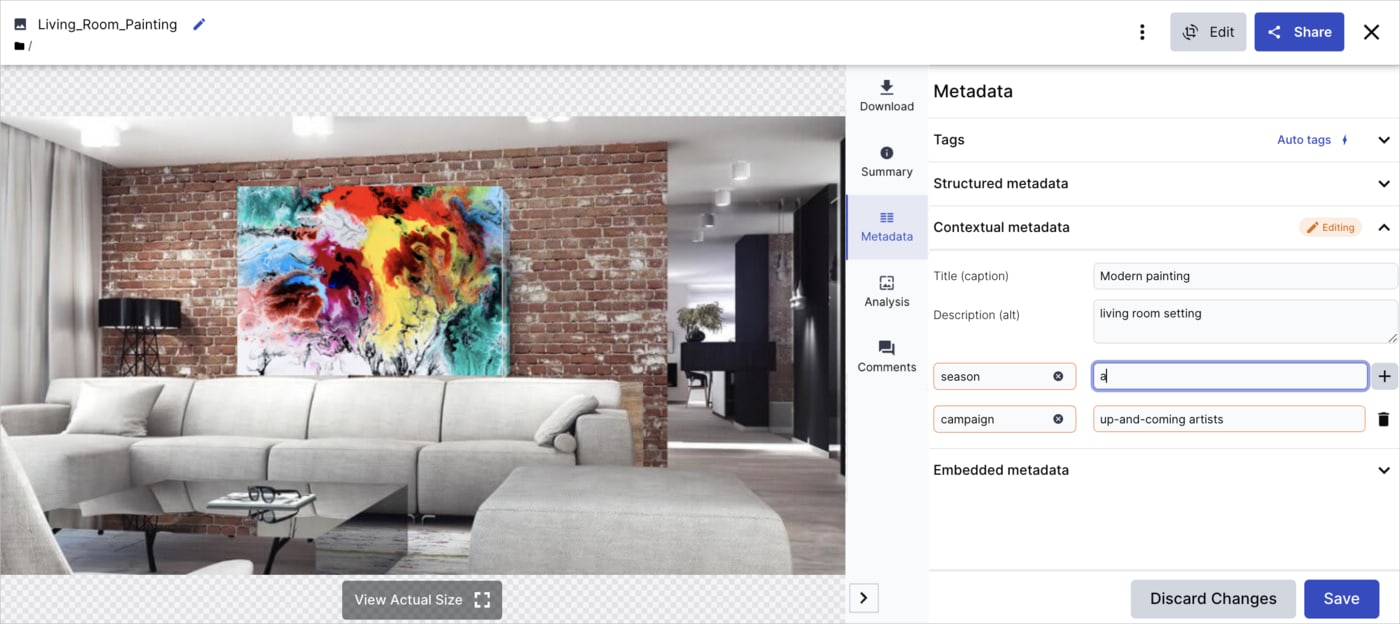
Using contextual metadata for text alternatives
The simplest approach is to use Cloudinary's built-in contextual metadata field, called alt, to store text alternatives. You can manage this field through the Media Library interface or programmatically via the APIs.
Here's an example of setting the alt contextual metadata field for an image during upload programmatically:
Alternatively, you can use any contextual metadata field name to store the text.
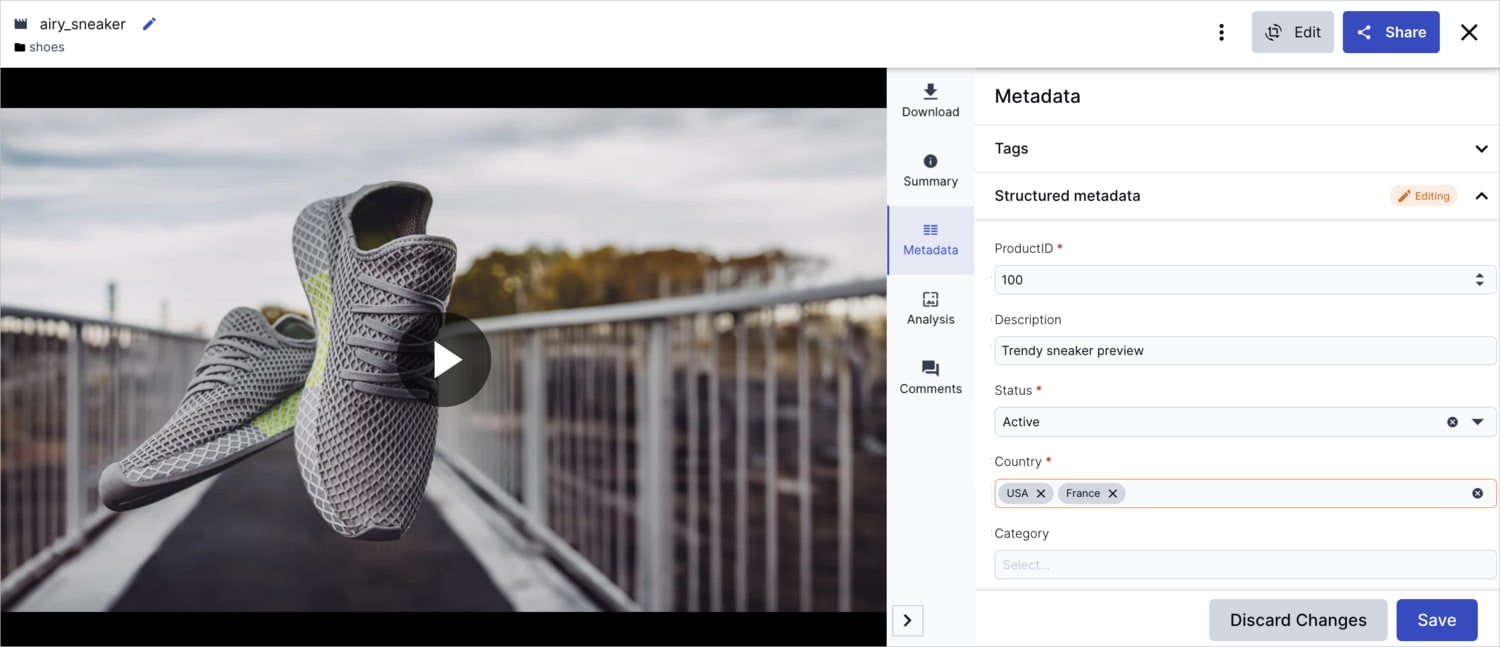
Using structured metadata for text alternatives
For better standardization across an organization, you can use structured metadata to create custom fields that support validation, approval workflows, and advanced search capabilities.
You can manage structured metadata fields through the Media Library interface or programmatically via the APIs.
Here's an example of setting a structured metadata field, with external ID, asset_description, on upload:
Centralized asset management benefits
By storing accessibility metadata directly with your assets in Cloudinary, you gain several key advantages, including:
- Single source of truth:
- All text alternatives are stored with the asset, ensuring consistency across all implementations
- No need to maintain separate databases or files for accessibility content
- Changes to descriptions automatically propagate to all applications using the asset
- Searchable and discoverable:
- Use the Search API method to find assets by their accessibility descriptions
- Identify assets missing alt text for remediation
- Analyze description quality across your Media Library
- Review and approval workflows:
- Content teams can review and approve accessibility descriptions in the Media Library
- Implement approval workflows before publishing content
- Bulk operations:
- Programmatically update multiple assets simultaneously
- Import accessibility descriptions from external sources
- Export descriptions for review by accessibility experts
Integrating with delivery
Once text alternatives are stored as asset metadata, they're automatically available in your delivery implementations:
JavaScript integration:
Product Gallery Widget integration:
This centralized approach ensures that accessibility improvements benefit all your applications simultaneously, while providing the tools needed for professional content management and review processes.
AI-based image captioning
While storing text alternatives as metadata provides centralized management, creating meaningful descriptions for large image libraries can be time-consuming. Using AI-based image captioning, you can programmatically provide captions for images, saving time and resources.
- Subscribe to the Cloudinary AI Content Analysis add-on.
-
Upload an image to your Media Library, invoking AI-based image captioning:
-
Use the AI-generated caption from the response for the alt text:
Example code:

Alternative ways to invoke AI-based image captioning:
- Define an upload preset in the Cloudinary Console settings, which you can use either programmatically, or in your Media Library, when uploading images.
- Use the Cloudinary Image Captioning block in MediaFlows to generate a caption as part of a workflow, for example, to update the
altcontextual metadata field on upload.
Learn how to build a PowerFlow that generates multilingual alt text.

- For images already in your Media Library, use the update method of the Admin API, instead of the upload method of the Upload API.
Cloudinary AI Vision
An alternative to AI-based image captioning is to use the Cloudinary AI Vision add-on. This has the benefit of analyzing images that are external to Cloudinary, or stored in Cloudinary product environments that you don't own. You just need a valid URL to the image.
- Subscribe to the Cloudinary AI Vision add-on.
-
Send a request to the Analyze API asking for a brief description of the image.
-
Use the AI-generated response for the alt text:
Example code:

 Ask AI
Ask AI